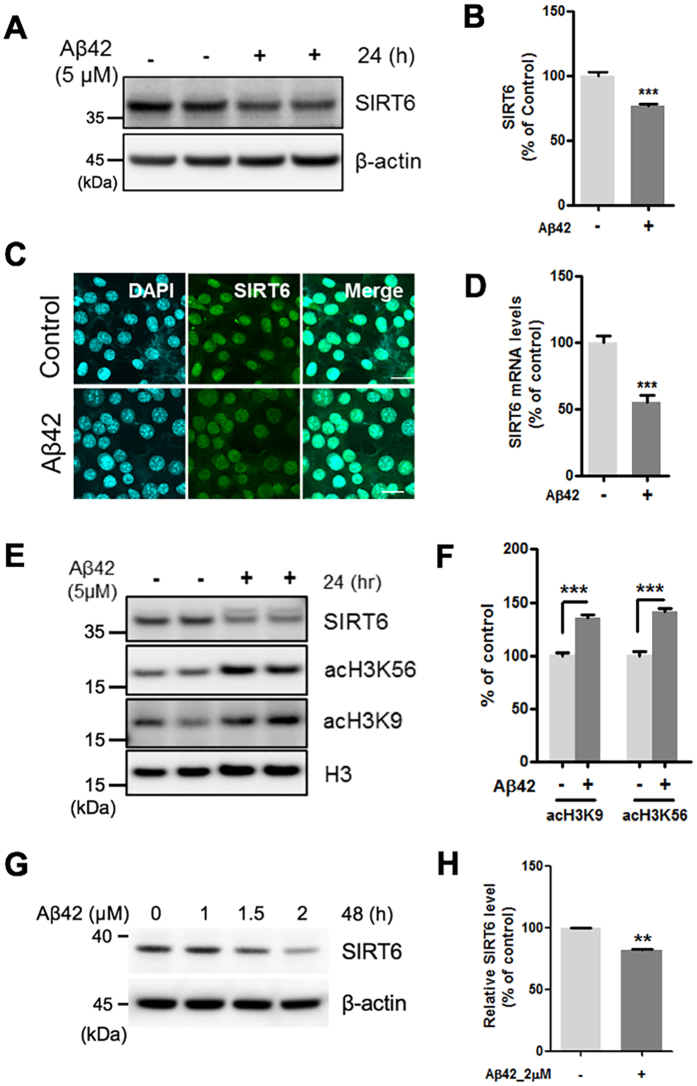
Figure 2. The effect of Aβ42 on the expression of SIRT6 and acetylation of H3K9 and H3K56.
HT22 cells were treated with Aβ42 (5 μM) for 24 h. Aβ42 decreased both the protein and the mRNA expression of SIRT6 and increased acetylation of H3K9 and H3K56. (A) Western blotting for SIRT6 protein in total protein from whole cell extracts. (B) Quantification of SIRT6 protein (n = 5, ***P < 0.001 versus vehicle, unpaired t-test). SIRT6 level was quantified by densitometry and normalized to β-actin. (C) Immunocytochemistry analysis for SIRT6. HT22 cells were stained with antibodies against SIRT6 (green). DAPI (blue) was used as a nuclear marker. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) The mRNA level of SIRT6 was measured by quantitative real-time PCR (n = 4, ***P < 0.001 versus vehicle group, unpaired t-test). (E) Western blotting for acetylation of H3K9 (acH3K9) and acH3K56. (F) Quantification of acH3K9 and acH3K56 (n = 4, ***P < 0.001, unpaired t-test). The levels of acH3K9 and acH3K56 were quantified by densitometry and normalized to histone H3. (G,H) Primary rat cortical neurons were treated with indicated concentration of Aβ42 for 48h. (G) Representative western blot image showing the changes in the expression of SIRT6. (H) Quantification of SIRT6 levels in the Aβ42-treated condition (2 μM, 48 h). n = 3, **P < 0.01 versus control, unpaired t-test. All the gels were run under same experimental conditions. Full-length images are presented in the supplementary information.