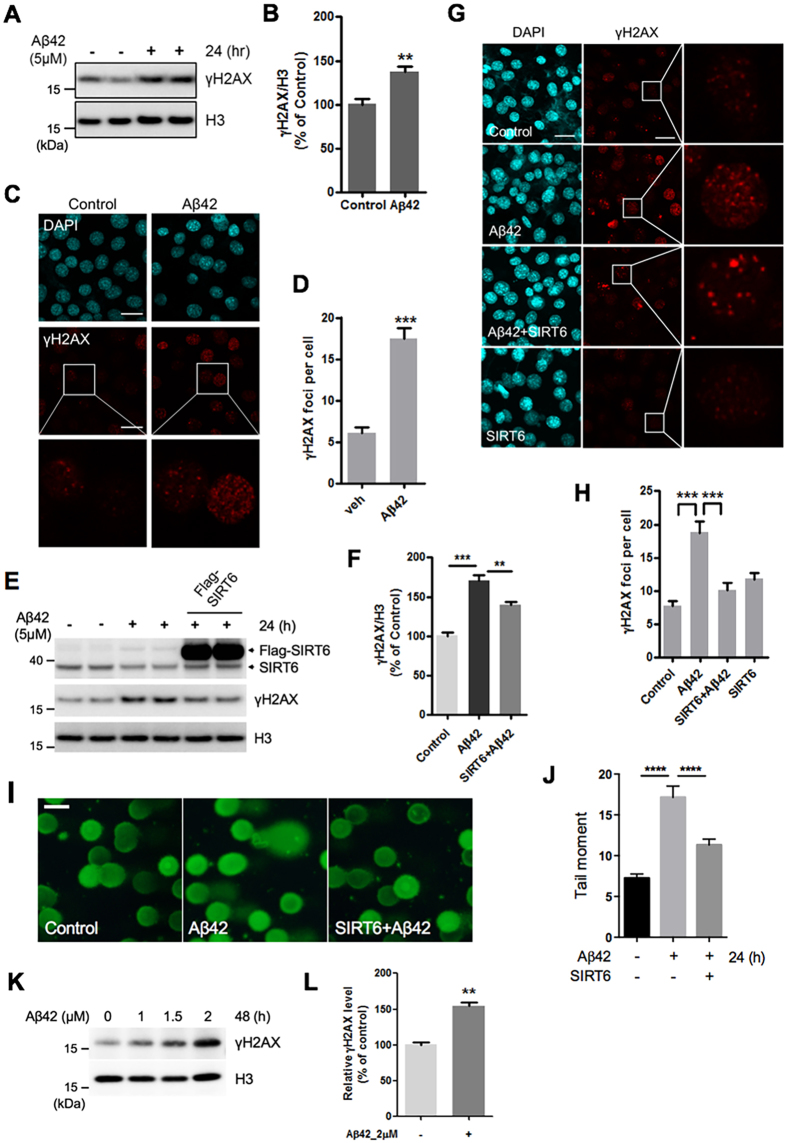
Figure 5. SIRT6 overexpression inhibits the DNA damage induced by Aβ42.
(A–D) HT22 cells were treated with Aβ42 (5 μM) for 24 h. (A,B) Representative immunoblotting image and quantitative analysis of γH2AX (n = 5, **P < 0.01, unpaired t-test). (C) Representative images of γH2AX (red) stained cells. After Aβ42 treatment, HT22 cells were stained with an antibody against γH2AX (red). DAPI (blue) was used as a nuclear marker. White boxes in the images indicate the area that is enlarged and shown at the bottom. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Quantification of γH2AX foci per cell detected in (C). The number of γH2AX foci was counted in 75 cells per each condition. ***P < 0.001, unpaired t-test. (E–J) HT22 cells were transiently transfected with Flag-SIRT6 24 h before Aβ42 treatment. (E) The expression level of each protein was assessed by immunoblotting. Histone H3 was used as a loading control. (F) Quantification of γH2AX levels. n = 4, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA ; Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (G) Representative images of γH2AX (red) stained cells. DAPI (blue) was used as a nuclear marker. Scale bar: 20 μm. (H) Quantification of γH2AX foci per cell detected in (G). The number of γH2AX foci was counted in 65 to 70 cells per each condition. ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA; Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (I) Representative alkaline comet assay image. DNA damage was assessed using an alkaline comet assay in HT22 cells. DNA was labeled with SYBR green dye. Scale bar: 100 μm. (J) The comet tail moments (tail DNA% × length of tail), expressed as DNA damage, were analyzed from at least 100 cells in each sample. ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA ; Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (K,L) Primary rat cortical neurons were treated with indicated concentration of Aβ42 for 48h. (K) Representative western blot image showing the changes in the expression of γH2AX. L. Quantification of γH2AX levels in the Aβ42-treated condition (2 μM, 48 h). n = 3, **P < 0.01, unpaired t-test. All the gels were run under same experimental conditions. Full-length images are presented in the supplementary information.