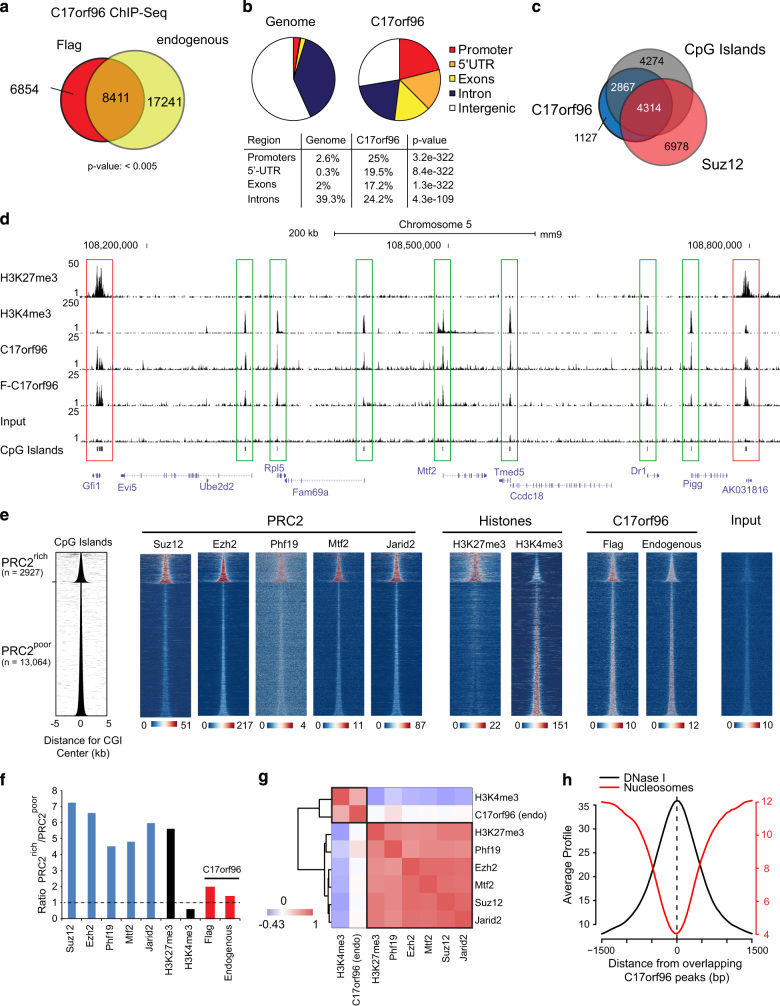
Figure 1.
C17orf96 is present at PRC2-rich and PRC2-poor CGIs. (a) Overlap of significant peaks (MACS, P<10−5) of ChIP-seq experiments performed in mES cells against Flag-mC17orf96 (using M2 beads) or the endogenous protein using a home-made antibody (Supplementary Figure S2). Overlapping peaks are considered has high-confident C17orf96-bound location. (b) C17orf96 is enriched at promoter regions, but depleted from intergenic regions. (c) C17orf96 peaks overlaps strongly with CGIs, but less with the PRC2 core component Suz12. (d) Example UCSC genome browser view, demonstrating that C17orf96-bound CGIs can be occupied by the repressive H3K27me3 [40] and active H3K4me3 histone marks. (F-C17orf96=Flag-C17orf96). (e) CGIs were categorized into PRC2-rich and PRC2-poor CGIs, based on the Suz12 data set [41]. Heatmaps of known PRC2 members [33, 42–44] at CGIs show a predominant presence at PRC2-rich CGIs, which correlates with presence of H3K27me3 [40] and reduced level of H3K4me3. C17orf96 is almost equally distributed between both groups. (f) Based on the average profiles that ratio of the factors between PRC2-rich /PRC2-poor CGIs has been calculated. The Flag-tagged C17orf96 protein is more dominantly bound at PRC2-rich CGIs than the endogenous protein. (g) Calculation of correlation coefficients between endogenous C17orf96, PRC2 members, H3K27me3 and H3K4me3 at CGIs demonstrates that C17orf96 correlates strongest with H3K4me3. (h) C17orf96 occupied locations are depleted for nucleosomes [45] and possess enhanced DNase I hypersensitivity [46].