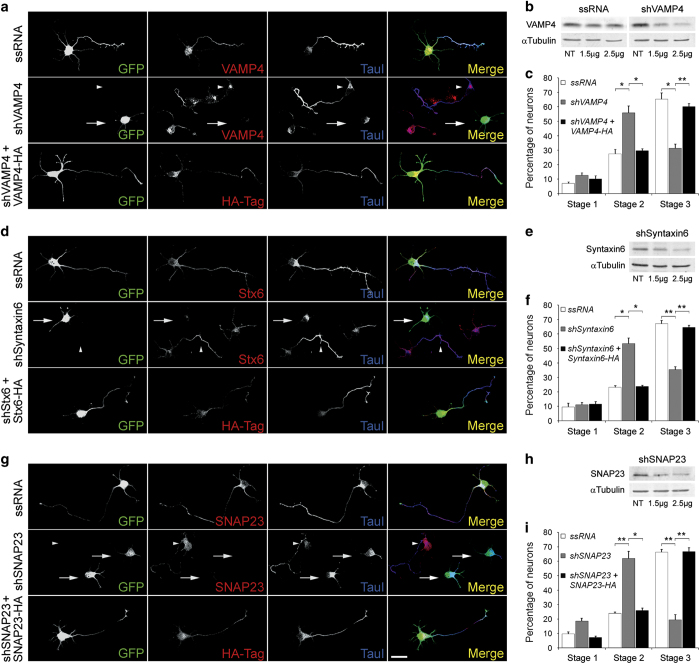
Figure 2.
(a) (first two rows) Double immunofluorescence micrographs of hippocampal neurons after 24 h in culture that show the localizations of VAMP4 (red) or tau-1 (blue) and GFP as a transfection marker. Note that the neurons transfected with VAMP4-targeted shRNA (second row, arrows) did not develop axons and did not target tau-1 to any particular neurite. Non-transfected neurons in the same culture exhibited tau-1- and VAMP4-positive axons (arrowheads). (bottom) Co-transfection with VAMP4-targeted shRNA plus wild-type, HA-tagged VAMP4 (red) rescued the phenotype. Outgrowth of a tau-1- positive axon (blue) is evident. (b) Western blots showing VAMP4 levels in rat brain glioma cells C6 transfected with ssRNA (left) and a VAMP4-targeted shRNA (right). Tubulin was used as a loading control. (c) Relative percentages (±s.e.m.) of control neurons or neurons containing VAMP4-targeted shRNA at specific stages of differentiation after 36 h in culture. n=3 independent experiments. At least 100 neurons were scored for each condition. (d) (first two rows) Double immunofluorescence micrographs of hippocampal neurons after 24 h in culture that show the localizations of Syntaxin6 (red) or tau-1 (blue) and GFP as a transfection marker. Note that the neurons transfected with Syntaxin6-targeted shRNA (second row, arrows) did not develop axons and did not target tau-1 to any particular neurite. Non-transfected neurons in the same culture exhibited tau-1- and Syntaxin6-positive axons (arrowheads). (bottom) Co-transfection with Syntaxin6-targeted shRNA plus wild-type, HA-tagged Syntaxin6 (red) rescued the phenotype. Outgrowth of a tau-1- positive axon (blue) is evident. (e) Western blots showing Syntaxin6 levels in rat brain glioma cells C6 cultured in the presence of a Syntaxin6-targeted shRNA. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (f) Relative percentages (±s.e.m.) of control neurons or neurons containing Syntaxin6-targeted shRNA at specific stages of differentiation after 36 h in culture. n=3 independent experiments. At least 100 neurons were scored for each condition. (g) (first two rows) Double immunofluorescence micrographs of hippocampal neurons after 24 h in culture that show the localizations of SNAP23 (red) or tau-1 (blue) and GFP as a transfection marker. Note that the neurons transfected with SNAP23-targeted shRNA (second row, arrows) did not develop axons and did not target tau-1 to any particular neurite. Non-transfected neurons in the same culture exhibited tau-1- and SNAP23-positive axons (arrowheads). (bottom) Co-transfection with SNAP23-targeted shRNA plus wild-type, HA-tagged SNAP23 (red) rescued the phenotype. Outgrowth of a tau-1- positive axon (blue) is evident. (h) Western blots showing SNAP23 levels in rat brain glioma cells C6 cultured in the presence a SNAP23-targeted shRNA (right). Tubulin was used as a loading control. (i) Relative percentages (±s.e.m.) of control neurons or neurons containing VAMP4-targeted shRNA at specific stages of differentiation after 36 h in culture. n=3 independent experiments. At least 100 neurons were scored for each condition. *P⩽ 0.005, **P⩽ 0.001. Calibration bar= 20 μm.