Figure 5.
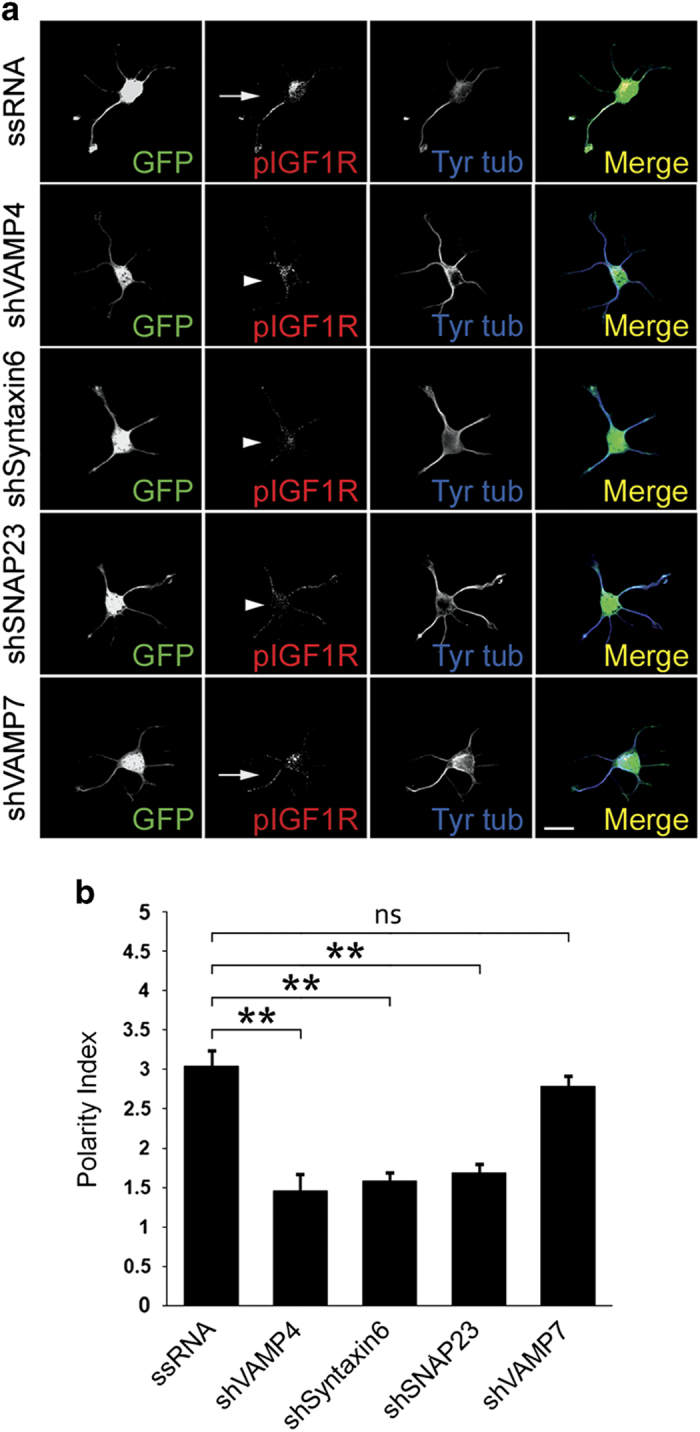
(a) Double immunofluorescence micrographs of hippocampal neurons (14 h in culture) that show the distributions of tyrosinated α-tubulin (blue), phosphorylated IGF-1 receptor (red), and the transfection marker GFP. Neurons were transfected with either a scrambled RNA sequence (ssRNA-top), VAMP4-targeted shRNA (second row), Syntaxin6-targeted shRNA (third row), SNAP23-targeted shRNA (fourth row) or VAMP7-targeted shRNA (bottom). Neurons were deprived of growth factors for 4 h and stimulated with 20 nM IGF-1 before fixation. Note the polarization of active (membrane-inserted) IGF-1 receptor to one of the minor neurites of the cell transfected with ssRNA (arrow-top) or transfected with VAMP7-targeteed shRNA (bottom). In contrast, neurons transfected with VAMP4, Syntaxin6 or SNAP23 (arrowheads-second, third and fourth rows fail to polarize the active IGF-1 receptor. (b) A ‘polarization index’ of active IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1r P.I.) was calculated as the fluorescence intensity (A.U.) of the brightest minor neurite/average fluorescence intensity (A.U.) of the other minor neurites of the same cell. Neurons were processed as in A). The polarization index is significantly higher in the neurons transfected with scrambled sequence RNA (*P=<0.01) compared to those transfected with VAMP4-, Syntaxin6- or SNAP-23-targeted shRNA. No significant differences in the polarization index were found in the neurons transfected with ssRNA and VAMP7-targeted shRNA. Scale bar, 20 μm.
