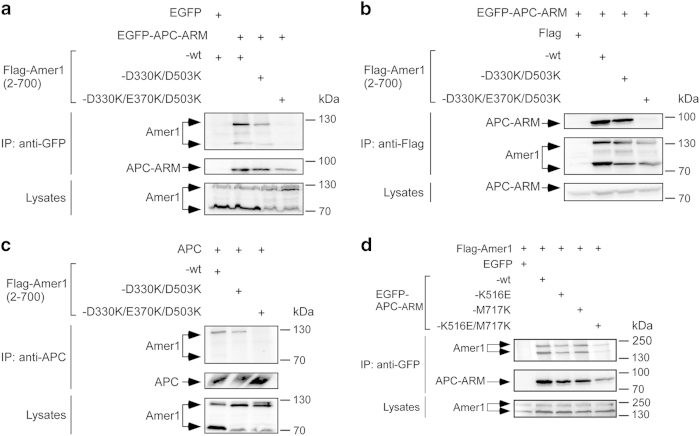
Figure 5.
Composite mutations in Amer1 or APC abolished the Amer1–APC interaction in cultured cells. (a, b) Co-immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that triple mutation of A1-D330K/A4-E370K/A2-D503K in Flag-tagged Amer1 (residues 2–700) attenuated its association with EGFP-tagged APC–ARM, using either anti-GFP (a) or anti-Flag (b) immunoprecitation followed by western blot analysis. Note that transfection of the Amer1 cDNA generates two protein bands that are due to alternative splicing (arrows [18]). (c) Triple mutation of D330K/E370K/D503K in Amer1 (2–700) destroyed its interaction with FL APC. (d) Double mutation of K516E (which abrogated A1/A2/A4-binding) and M717K (which impaired A3-binding) in APC–ARM reduced its association with FL Amer1 by 60% as determined by densitometric analysis.