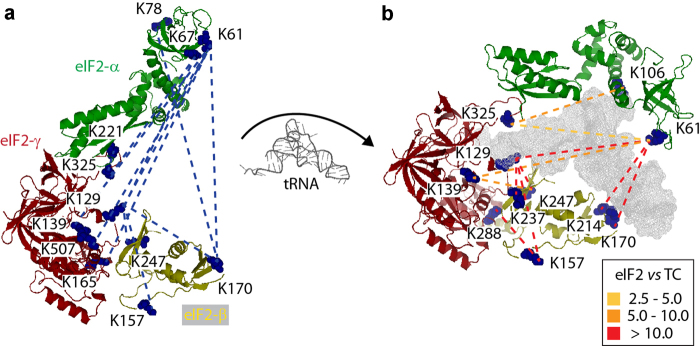
Figure 3.
Cross-linking of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2) and formation of the ternary complex. (a) The homology models of α-, β- and γ-subunits were aligned with the archaeal homologue of eIF2 (PDB ID 3CW2). Cross-linking apo eIF2 reveals several interactions between the α-subunit and β- and γ-subunits, showing that eIF2 is highly flexible in solution. (b) Homology models of α-, β- and γ-subunits were aligned with the archaeal homologue of the ternary complex (TC; PDB ID 3V11). Comparative cross-linking of apo eIF2 versus the TC reveals multiple inter-subunit cross-links with reduced intensities after binding Met-tRNAiMet. Changes in cross-linking intensities are colour coded; values 2.5–10 represent cross-linking intensities that are higher in eIF2 compared with the TC.