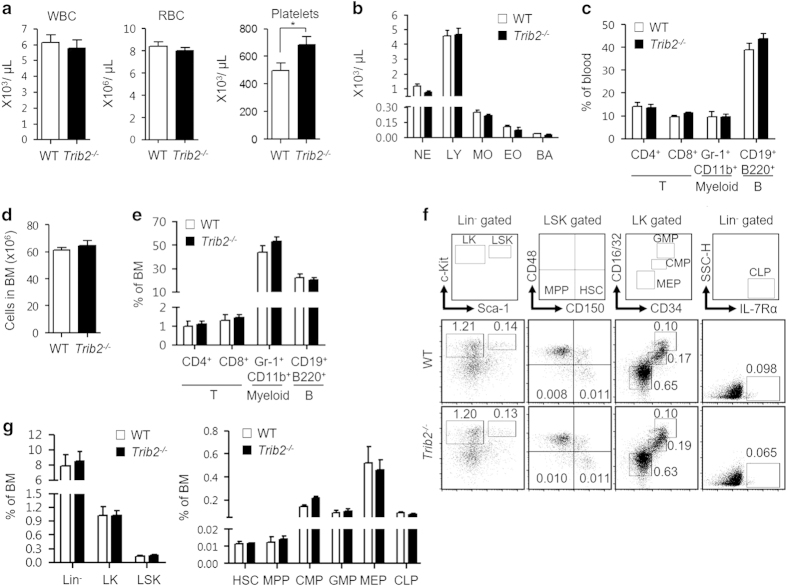
Figure 1.
TRIB2 loss does not affect murine hematopoiesis in bone marrow. Complete blood counts (a) and WBC differential counts (b) of WT (n=13) and Trib2−/− (n=22) mice were determined by hematology analyzer. BA, basophils; EO, eosinophils; LY, lymphocytes; MO, monocytes; NE, neutrophils. (c) The distribution of mature myeloid, B and T-cells in the blood of WT (n=3) and Trib2−/− (n=10) mice were measured by flow cytometry using the indicated lineage specific cell surface markers. (d) BM cellularity (n=5–7 per genotype) was counted by trypan blue exclusion after RBC lysis of the cell suspension collected from two pelvises, femurs and tibias. (e) The distribution of myeloid, B and circulating T-cells in the BM of WT (n=3) and Trib2−/− (n=9) mice. (f) Immunophenotyping of HSPCs populations (HSC, MPP, CMP, GMP, MEP and CLP) in BM. Each sub-population is indicated in the outlined areas (top row). The corresponding values in the representative staining profile of WT (middle row) and Trib2−/− (bottom row) mice (n=3 per genotype) are frequency of BM and graphed in g. CLP, Lin−IL-7Rα+; CMP, LK CD34+CD16/32lo; GMP, LK CD34+CD16/32hi; HSC, LSK CD150+CD48−; Lin, lineage; LK, Lin−c-Kit+; LSK, Lin−Sca-1+c-Kit+; MPP, LSK CD150−CD48−; MEP, LK CD34−CD16/32−; SSC-H, side scatter-height. For a, unpaired Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis. *P<0.05, all quantified data are presented as mean and s.e.m. CMP, common myeloid progenitor; CLP, common lymphoid progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-macrophage progenitor; MEP, megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitor; MPP, multipotent progenitor; RBC, red blood cell; WBC, white blood cell.