Figure 5. Immature SST interneurons broadly innervate deep cortical layers.
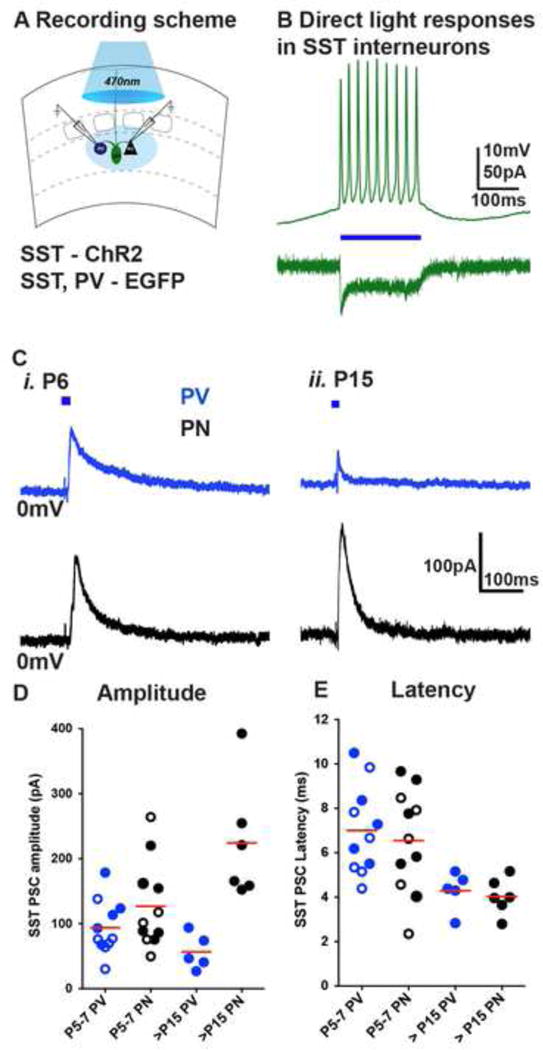
(A) ChR2 was targeted to SST interneurons by SSTCRE; Ai32ChR2-EYFP; Lhx6EGFP mouse line or AAV-flex-hChR2.mCherry virus injections into infragranular layers of SSTCRE; Lhx6EGFP mice and synaptic currents in Lhx6EGFP positive PV interneurons and adjacent PNs in the L5A/6B of barrel cortex recorded at 0mV holding potential, in the presence of NBQX (10μM) and DAP-5 (25μM). (B) Light (blue horizontal bar, 100ms) induced responses in SST interneurons. (C) Representative traces of SST interneuron evoked responses (5ms light pulses) in PV interneurons (blue) and PNs. (D) Representative fluorescent image of a P6 coronal slice containing ChR2-mCherry expressing SST interneurons 5 days after AAV-flex-hChR2.mCherry virus injections into infragranular layers of SSTCRE; Lhx6EGFP mice. (E) Light evoked synaptic currents at P6 in Lhx6EGFP positive PV interneurons and adjacent PNs in the L5A/6B of barrel cortex recorded at 0mV holding potential, in the presence of NBQX (10μM) and DAP-5 (25μM), blue horizontal bar indicates 10ms light pulse. (F) SST-PSC amplitudes in PV interneuron (transgenic closed circles, n=5; virus open circles, n=6) were similar in PNs (transgenic closed circles, n=6; virus open circles, n=5) at P5–6 (p>0.05), while PV interneuron (transgenic, n=5) were significantly smaller than PNs (transgenic, n=6) at P15–18 (p<0.0001). G) Latency of light-evoked IPSCs (ms) were similar among PV interneurons and PNs (p>0.05). For each time point, n=2 animals, n=2 brain slices were analyzed per animal, Mann-Whitney test
