Figure 5. mosGCTLs are antagonists for AMP-mediated bacterial elimination.
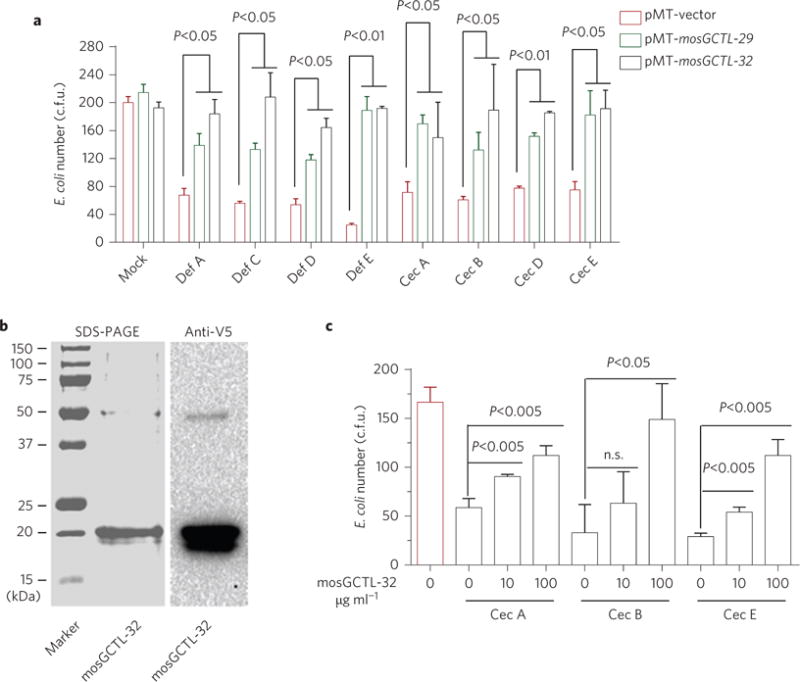
a, mosGCTL-29 and mosGCTL-32 expressed in S2 supernatant interrupted AMP-mediated bacterial elimination. The empty-vector-transfected S2 supernatant with AMPs served as the mock control. The S2 supernatant with mosGCTLs and/or AMPs was individually mixed with the E. coli cells. b, Expression and purification of mosGCTL-32 using a Drosophila S2 cell expression system. c, The purified mosGCTL-32 protein antagonized Cec-mediated bacterial killing. The purified recombinant mosGCTL-32 protein was pre-incubated with the E. coli cells, and subsequently the synthesized Cec peptides were added to the cells. The same concentration of BSA was used as the mock control. a,c, After 2 h of incubation, E. coli viability was assessed by the c.f.u. assay. Data are represented as mean±s.d. in each group and analysed using the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. All experiments were biologically repeated three times with similar results.
