Fig. 4.
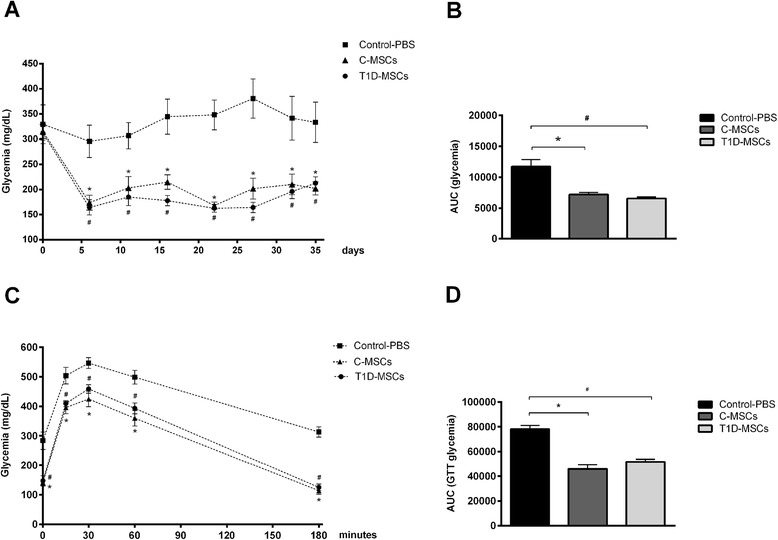
Intrasplenic injection of T1D-MSCs promotes reversion of hyperglycemia and improvement of peripheral response to glucose in STZ-induced diabetic mice. T1D-MSCs or C-MSCs (1 × 106) were administered by intrasplenic injection in diabetic mice 20 days after diabetes induction. a Blood glucose levels (mg/dl) were frequently measured in nonfasting mice for 35 days. A reduction in blood glucose levels was observed in 67 % (6/9) of diabetic MSC-treated mice mainly on day 6 post transplantation (only the glycemic levels of responder mice/n = 6 are shown). The control group was treated with intrasplenic injection of PBS (Control-PBS, n = 6). b Area under the curve of glycemia (AUC) from day 0 to day 35. The AUC was determined for each animal, and the mean ± SD of each group is shown. c Glucose tolerance tests (GTT) were performed in 10-hour fasted mice, 30 days after T1D-MSC, C-MSC, or PBS intrasplenic administration. Glucose (1.5 mg/g) was intraperitoneally administered and blood glucose levels (mg/dl) were determined 0, 15, 30, 60, and 180 minutes after administration. d AUC during GTT was determined for each animal and the means ± SD of each group is shown. *P <0.05 (Control-PBS × C-MSCs); # P <0.05 (Control-PBS × T1D-MSCs). C-MSCs mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow of healthy individuals, PBS phosphate-buffered saline, T1D-MSCs mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow of newly diagnosed T1D patients
