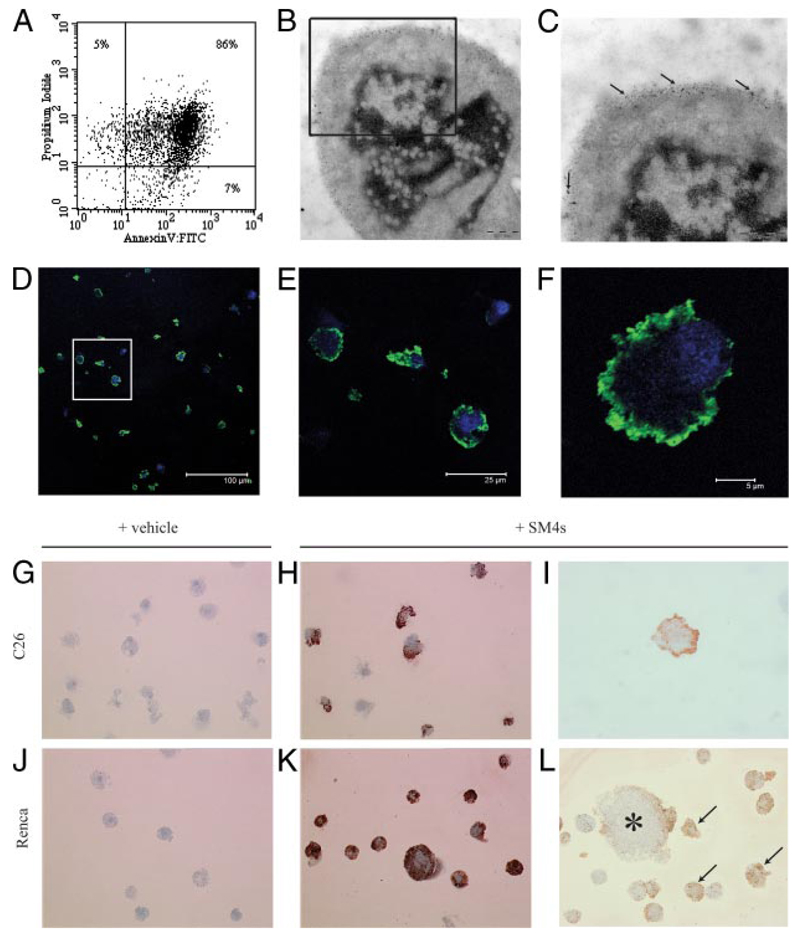
FIGURE 2. C26 and Renca cells demonstrate late apoptotic phenotype after induction with staurosporine and successful SM4s painting after exposure to SM4s.
A, C26 cells were incubated with staurosporine (1 µM) for 24 h. PS exposure and membrane permeability were detected by flow cytometry using FITC-conjugated annexin V and PI, respectively. Annexin V/PI double-positive cells were considered as late apoptotic. B, Electron photomicrograph of apoptotic C26 cell with evident nuclear condensation and fragmentation (Zeiss, ×30000). B and C, Electron photomicrographs of apoptotic C26 cells preincubated with 10 µM SM4s. Gold particle-conjugated goat anti-mouse Ab (particle size of 6 nm) was used for visualization of the sulfatide (arrows). D–F, Apoptotic C26 cells were prepared as described above, spun down, stained with DRAQ5 (nucleus), and immunostained with anti-O4 and AlexaFluor 488 donkey anti-mouse IgG (H+L) mAbs (SM4s). F, Confocal image of a single cell shows predominant membrane localization of the sulfatide (×5000). Data are presented as merge of green and blue channels. G–L, Apoptotic cells subjected to immunocytochemistry analysis with anti-O4 mAb. Photomicrographs of apoptotic cells treated with sulfatide or vehicle (DMSO). G and J, C26 and Renca control cells (Leica, ×400). H and I, C26 cells treated with 10 µM SM4s (Leica, ×400 and ×1000, respectively). K, Late apoptotic Renca cells painted with sulfatide (Leica, ×400). L, Binding of SM4s to plasma membrane of late apoptotic (arrows) and early apoptotic (star) Renca cells (Leica, ×400).