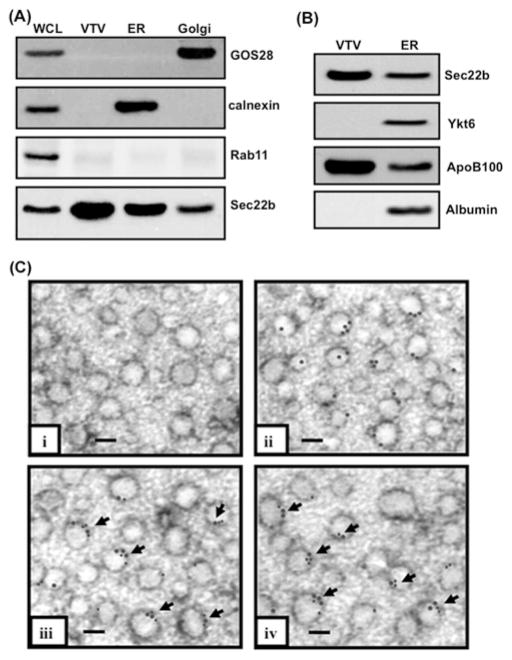
Figure 1. Sec22b concentrates on VTVs and co-localizes with p58 and Sar1 on their surface.
(A) Samples containing hepatic whole-cell lysate (WCL), VTVs, ER and Golgi (each containing30 μg of protein) were separated by SDS/PAGE (12 % gel), transblotted on to a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with specific antibodies against GOS28, calnexin, and Rab11. For details, see the Experimental section. Protein detection was by ECL. (B) Samples of ER and VTVs (30 μg of protein each) were separated by SDS/PAGE (5–15 % gel), transblotted on to a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with specific antibodies against Sec22b, Ykt6, ApoB100 and albumin. Protein detection was by ECL. (C) Immunoelectron microscopy of VTVs utilizing the negative-staining technique. VTVs were adsorbed on formvar-carbon-coated nickel grids and were treated with: (i) anti-rabbit pre-immune IgG; (ii) rabbit polyclonal anti-Sec22b antibodies detected with anti-(rabbit IgG) labelled with 15 nm gold particles; (iii) mouse anti-Sec22b antibodies detected with anti-(mouse IgG) labelled with 15 nm gold particles and anti-Sar1 antibodies detected with anti-(rabbit IgG) labelled with 10 nm gold particles (arrows show co-localization of Sec22b with Sar1); and (iv) anti-p58 antibodies detected with anti-(rabbit IgG) labelled with 10 nm gold particles and mouse anti-Sec22b antibodies detected with anti-(mouse IgG) labelled with 15 nm gold particles (arrows show co-localization of Sec22b with p58). Scale bars, 100 nm.