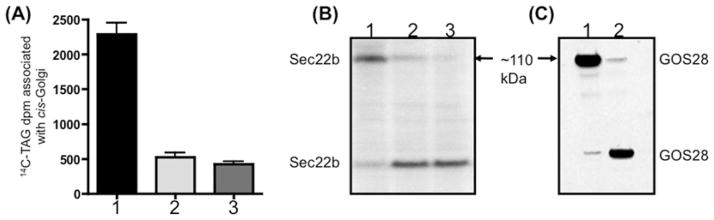
Figure 7. Incubation of VTVs with anti-Sec22b antibodies or hepatic Golgi with anti-GOS28 antibodies blocks VTV–Golgi docking and SNARE complex formation.
(A) VTVs (150 μg of protein) containing [14C]TAG were incubated at 4 °C with 10 μl of pre-immune IgG (bar 1) or 10 μl of anti-Sec22b antibodies (bar 2) for 1 h at 4 °C. Hepatic cis-Golgi (300 μg of protein) was incubated at 4 °C with 10 μl of anti-GOS28 antibodies (bar 3). In each case, the excess antibodies were removed by washing. After antibody treatment, non-radiolabelled cis-Golgi was added to tubes containing IgG-treated VTV (bar 1), Sec22b antibody-treated VTV (bar 2) and untreated [14C]TAG-loaded VTVs were added to tubes containing antibody-treated cis-Golgi (bar 3). The VTV–Golgi docking reaction was carried out and the post-docking Golgi membranes were separated, and Golgi-associated [14C]TAG levels were measured. Results are means + S.E.M. (n = 4). (B) Post-docking Golgi membranes from (A) were solubilized in Laemmli buffer, and proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and probed with anti-Sec22b antibodies. Lanes 1–3 represent the same docking conditions as applied in bars 1–3 in (A) respectively. (C) Post-docking Golgi membranes from (A) (bars 1 and 2) were solubilized in Laemmli buffer and proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and probed with anti-GOS28 antibodies. Lanes 1 and 2 represents the same docking conditions as used in bars 1 and 2 in (A) respectively.