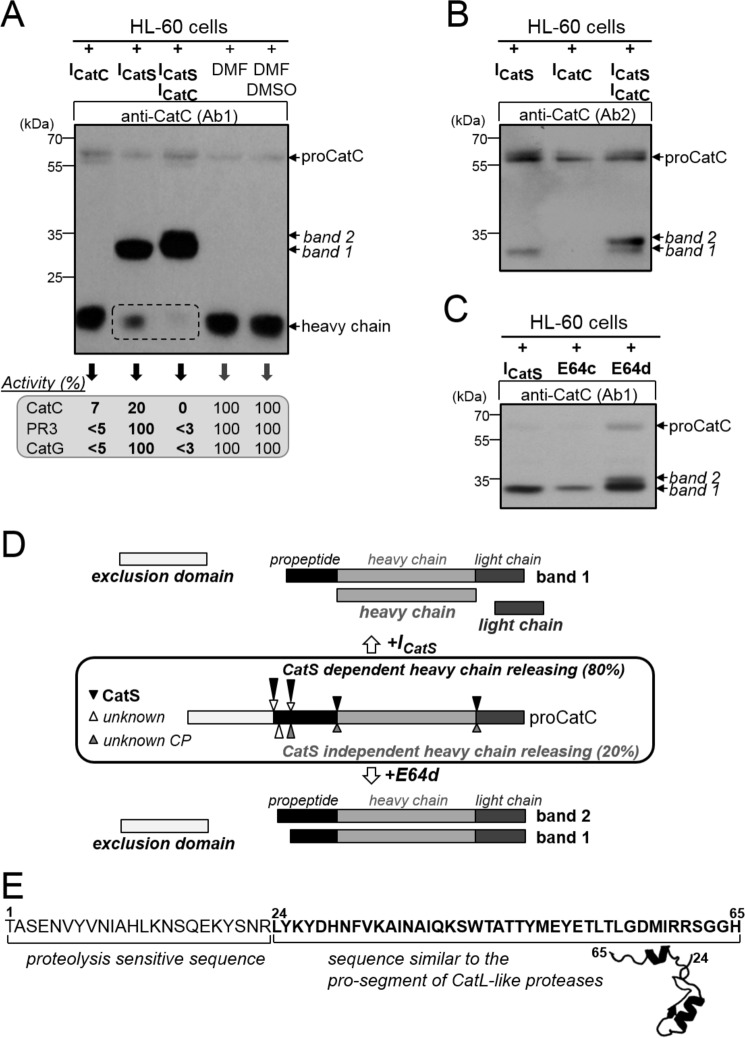
FIGURE 7.
Processing of proCatC in HL-60 cells cultured with or without synthetic inhibitors. A, HL-60 cells were cultured for 1 week in medium containing ICatS (10 μm), ICatC (2 μm), ICatS/ICatC (10 μm/2 μm), DMF, or DMSO/DMF, and then total cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-CatC antibody (Ab1). The percentages of residual CatC, PR3, and CatG activity toward their respective selective substrates were given in the box. B, HL-60 cells were cultured for 1 week in medium containing ICatS (10 μm), ICatC (2 μm), and ICatS/ICatC inhibitors (10 μm/2 μm), and their lysates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-CatC antibody (Ab2). C, HL-60 cells were cultured for 48 h in medium containing ICatS (10 μm), E64c (100 μm), or E64d (100 μm), and then total cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-CatC antibody (Ab1). Similar results were observed in five independent experiments. D, diagram summary showing the processing of proCatC in HL-60 cells cultured in the presence of ICatS or E64d. Arrows indicate the position of proteolytic cleavages in proCatC. CP, cysteine protease. E, partial sequence of the CatC propeptide (residues 1–65) showing the N-terminal proteolysis-sensitive extension (residues 1–24) and the structurally conserved sequence found in CatL-like cysteine proteases (residues 24–65). Model structure was obtained using cysteine peptidase C (PDB code 4HWY; Ref. 37) as a template.