FIGURE 4.
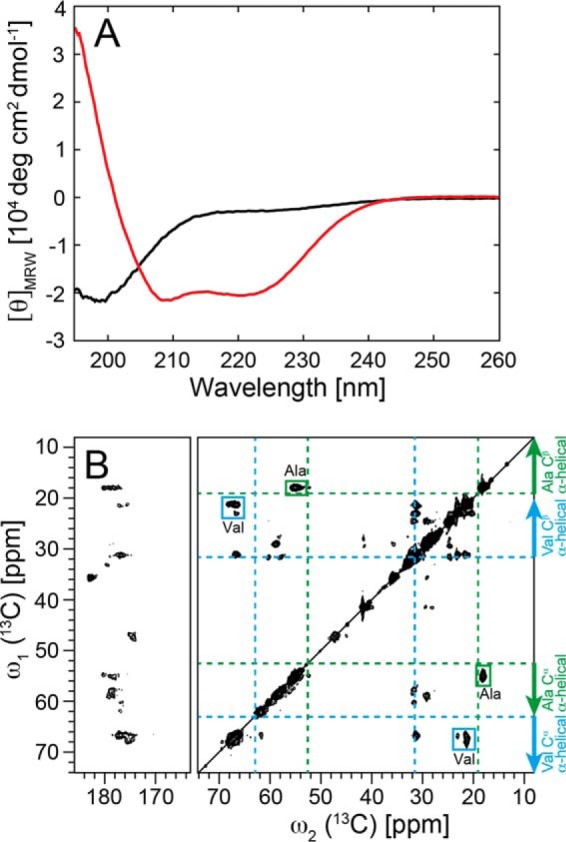
Helical secondary structure of α-Syn in lipoprotein particles. A, conformational change of α-Syn determined by CD from a predominantly unfolded state (black) free in solution to an α-helical state in α-Syn DOPS lipoprotein particles (red). For the α-Syn DOPS lipoprotein particles, the size exclusion chromatography fraction 9.5–10 ml (Fig. 1A) was used. B, two-dimensional 13C DARR solid-state NMR spectra (at a magnetic field of 850 MHz 1H frequency) of uniformly 13C, 15N-labeled α-Syn DOPS lipoprotein particles. The assigned cross peaks from Ala and Val residues are indicated by green and cyan boxes, respectively. Indicated with dotted green and cyan lines are the random coil 13Cα, 13Cβ chemical shifts for the amino acid residues Ala and Val, respectively. Arrows show the chemical shift area typically observed for α-helical secondary structure.
