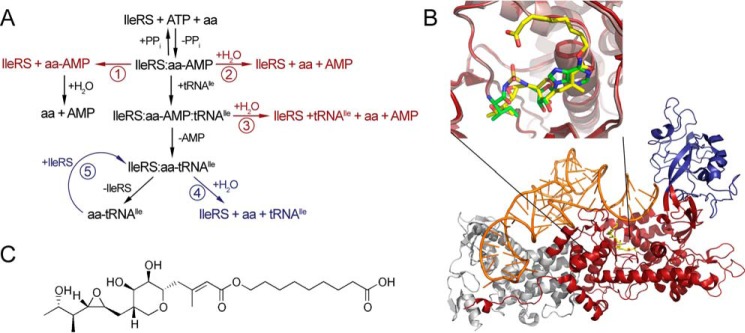
FIGURE 1.
Structure of enzymatic pathway of IleRS. A, schematic presentation of enzymatic reactions. The central pathway, colored in black, represents amino acid activation, tRNA binding, aminoacyl transfer, and dissociation of aminoacylated tRNA from the enzyme. Editing pathways are shown to the left and right. Pre-transfer editing may proceed through enhanced dissociation of non-cognate aminoacyl-AMP (pathway 1) or through its enzymatic hydrolysis, which may be tRNA-independent (pathway 2) or tRNA-dependent (pathway 3). Misaminoacylated tRNA is deacylated through post-transfer editing, in cis (pathway 4) or in trans (pathway 5). Editing reactions occurring in synthetic site are colored in red, and the ones taking place in the editing domain are colored in blue. B, structure of S. aureus IleRS in complex with mupirocin and tRNAIle (Protein Data Bank code 1FFY). Synthetic domain is colored in red, editing domain in blue, tRNAIle in orange, and mupirocin in yellow. The inset shows overlapped structures T. thermophilus synthetic site with mupirocin in yellow (Protein Data Bank code 1JZS) and Ile-AMS in green (Protein Data Bank code 1JZQ). C, mupirocin structure.