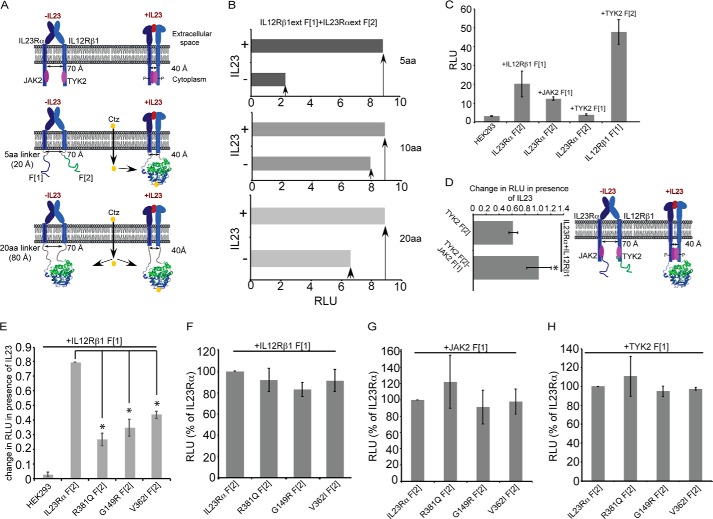
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of IL23R activation mechanism model. A, schematic representation of allosteric IL23R activation. IL23R exists as a heterodimer before interaction with IL23 cytokine similar to the EpoR receptor (36, 62). The extracellular domain exists in a conformation that keeps the intracellular domains and associated JAK2 and TYK2 separated from each other by ∼70 Å. Upon binding to IL23, the extracellular dimer is reorganized and brings the intracellular cytoplasmic domains within ∼ 40 Å of each other, allowing for interaction between and activation of their associated kinases. For identification of IL23R activation mechanism, the extracellular and transmembrane domains of IL23R and IL12Rβ1 are fused to Renilla luciferase (Rluc) complementary N- and C-terminal fragments, Rluc F[1] and F[2], via flexible linkers consisting of 1, 2, or 4 five-amino acid repeats to generate the following: IL23R and IL12Rβ1 fused to 5-, 10-, and 20-amino acid linkers that are in turn fused to the Rluc fragments. HEK293 cells transfected with these receptor fusions and PCA were detected by measuring the luminescence. When the receptors are fused via a 5-aa linker, folding of the Rluc reporter protein from the fragments only occurs for the IL23 hormone-bound active form of the receptor dimer. If receptors fused to Rluc fragments via 10- or 20-aa linkers, Rluc reporter protein can fold from the fragments in either inactive or active dimer conformations. The structural model of Renilla luciferase was rendered using information from 2pSj.pdb (63) using PyMOL 1.3. B, Rluc enzyme assay detected the IL23R activation in HEK293 cells. Cells were co-transfected with IL23Rα and IL12Rβ1 fused to Rluc PCA fragments via various linker lengths. The next day the cells were incubated with and without 100 ng of IL23 cytokine followed by measurement of Rluc enzyme activity using benzyl coelenterazine as the substrate and detection using a luminometer. The signal is expressed as relative light units (RLU). C, Rluc PCA reveals the interaction between IL23Rα and their subunits and their associated kinases (JAK2 and TYK2). HEK293T cells were transfected with pCDNA3.1 harboring the cDNA of full-length IL23R receptor subunits and the kinases JAK2 and TYK2 fused to Rluc fragments to detect the interaction as measured by PCA (RLU) of Rluc. D, JAK2 and TYK2 association in the presence of IL23 binding to IL23R was detected by Rluc PCA. Rluc fragments were fused to JAK2 and TYK2 and were co-transfected in HEK293T cells stably expressing IL23R subunits followed by measuring Rluc luminescence. Statistical significance denoted by the asterisk (*) was calculated by Student's t test, where p < 0.05. E, IL23Rα variants show the reduction in activation by IL23. IL23Rα, its, variants and IL12Rβ1 were fused to Rluc fragments to detect activation by IL23 (10 ng/ml), and luminescence was measured as in B. The change in RLU between cells not treated and treated with IL23 was calculated, and activation was thus observed as a function of change in RLU. Statistical significance denoted by the asterisk (*) was calculated by ANOVA, where p < 0.01. F, G, and H, IL23Rα variants retain their ability to interact with IL12Rβ1, JAK2, and TYK2. IL23Rα and variants Rluc fragment 2 (F[2]) fusions were co-transfected with either IL12Rβ1 fused to Rluc fragment 1 F[1], IL12Rβ1 F[1] (F), JAK2 F[1] (G), and TYK2 F[1] (H), and reconstitution of Rluc enzyme activity was measured to assess their interaction. Rluc enzyme activity (RLU) is expressed as percentage relative to IL23Rα. Data and S.D. are representative of three independent experiments.