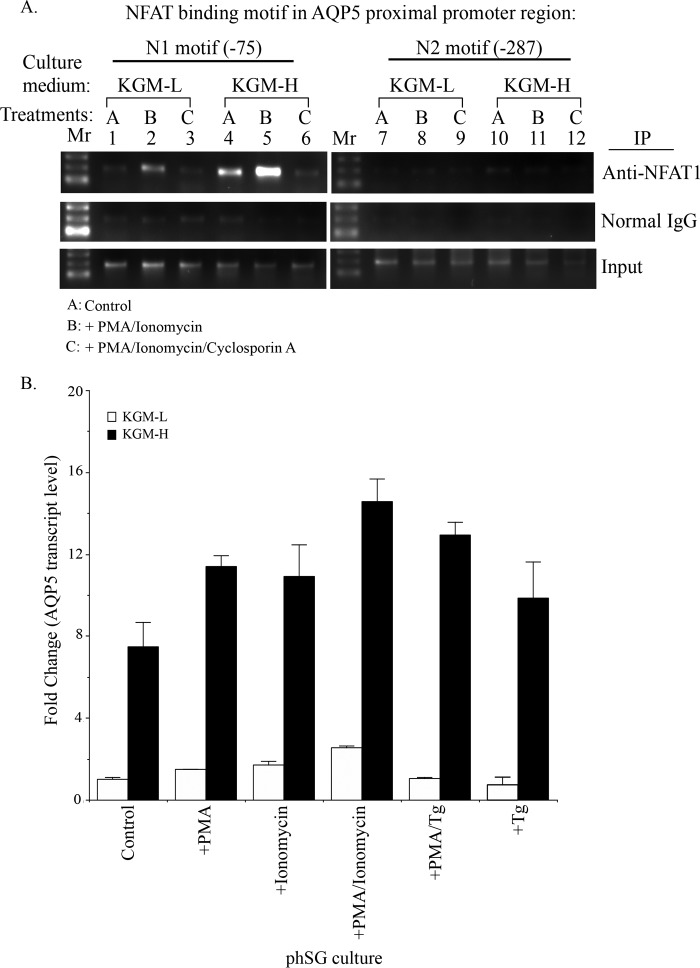
FIGURE 6.
A, high [Ca2+] medium promotes binding of NFAT1 to the AQP5 promoter in response to activation of Ca2+ signaling. phSG cells were treated for 45 min either with PMA + ionomycin (10 ng/ml and 0.1 μm, respectively) (B), or together with cyclosporin A (10 nm) (C), or without treatment, control (A), in KGM-L or in KGM-H medium. Cells were collected for ChIP analysis using NFAT1 antibody or normal mouse IgG as control for pull-down and assessed using PCR (described under “Experimental Procedures”). Mr, DNA molecular weight ladder; N1 and N2, the positions of NFAT consensus motifs 75 and 287 bp upstream of the transcription initiation site, respectively. B, expression of AQP5 in phSG cells treated with PMA, ionomycin, and Tg. phSG cells were cultured in KGM-L or KGM-H for 2 days and then treated with PMA, ionomycin, or PMA/ionomycin for 4 h or with PMA/Tg or Tg for 15 min. Following this incubation, the reagent-containing media were replaced with the respective growth media (minus reagent), and cells were further maintained for 48 h. Total RNA was isolated, and the expression level of AQP5 transcript was monitored by TaqMan probe or quantitative real-time PCR assay. Data are presented as -fold change (mean ± S.E.) of triplicate samples from three separate experiments relative to that of control conditions in KGM-L.