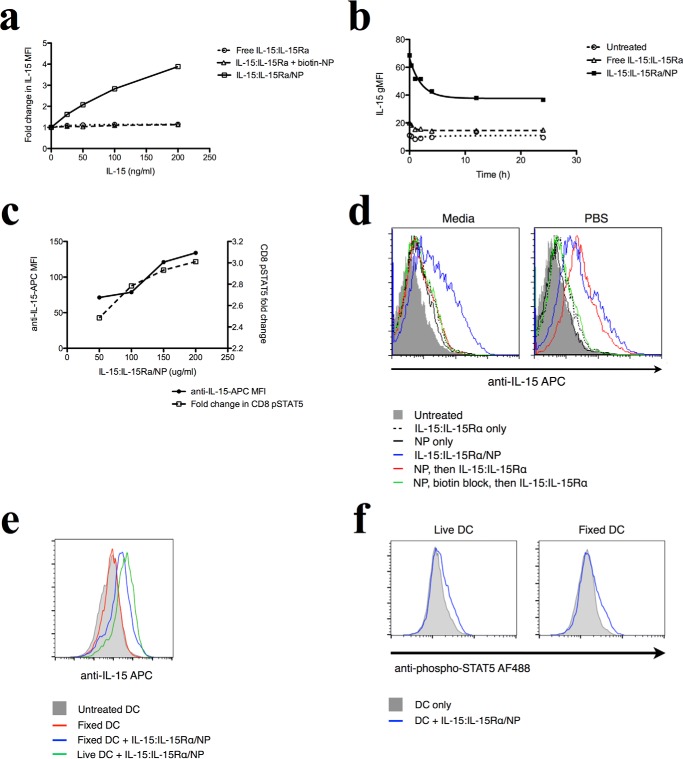
FIGURE 6.
Delivered NP-bound IL-15 is retained on the surface of DCs and signals CD8+ T cells. a, DCs were incubated with different concentrations of free or NP-bound IL-15:IL-15Rα constructs for 2 h and then stained for human IL-15. b, to track the fate of surface-retained IL-15 on DCs over time, DCs were incubated with 150 ng/ml of free or NP-bound IL-15 for varying amounts of time and then fixed and stained for human IL-15. c, DCs were incubated with different levels of IL-15:IL-15Rα-bound nanoparticles for 1 h and then washed and incubated with purified CD8 T cells for 1 h. CD8 cells were fixed and stained for phosphorylated STAT5. d, to determine whether avidin binding sites are detectable on the surface of NP-treated cells, DCs were incubated with NPs in PBS for 1 h and then exposed to biotinylated IL-15. IL-15/NP was given as a positive control, and some cells were blocked with biotin after NP binding to saturate avidin binding sites. This experiment was performed in both media and PBS. e, fixed and live DCs were co-incubated with IL-15-coated NPs for 2 h and then washed extensively and used to stimulate purified CD8+ T cells. T cells were then stained for phospho-STAT5. Curves where IL-15 was present are shown in blue, and control cells are shown in gray. f, fixed and live DCs were co-incubated with IL-15-coated NPs for 2 h and then washed and stained for IL-15.