FIGURE 8.
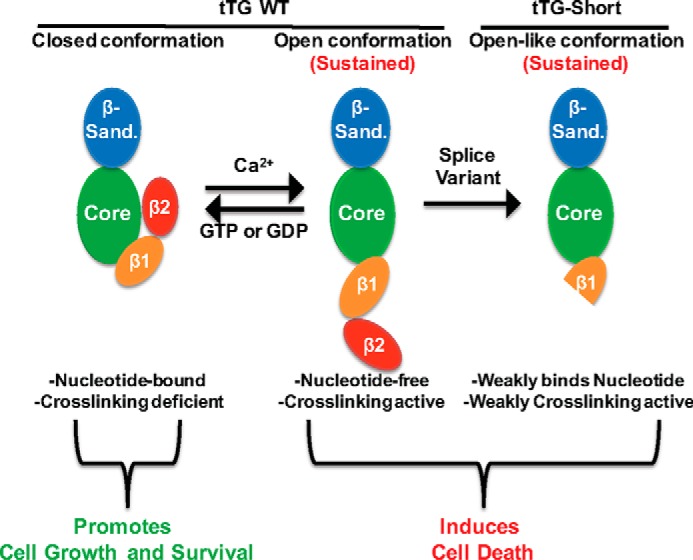
Diagram highlighting the different conformational states of tTG and the effects they have on cells. tTG WT primarily adopts a closed conformation in cells due to the relatively high levels of GTP or GDP and low levels of Ca2+ (left panel). Under these conditions tTG has been shown to promote cell growth and survival. However, in response to cell stresses, intracellular Ca2+ levels can be increased, resulting in less GTP/GDP binding to tTG and allowing for it to adopt an open, catalytically active conformation (middle panel). If tTG persists in the open conformation for extended lengths of time, it induces cell death. Interestingly, tTG-Short is a splice variant of tTG that lacks the portion of the C terminus determined to be important for keeping it in the closed conformation. Consistent with this finding, tTG-Short expression in cells induces apoptosis (right panel).
