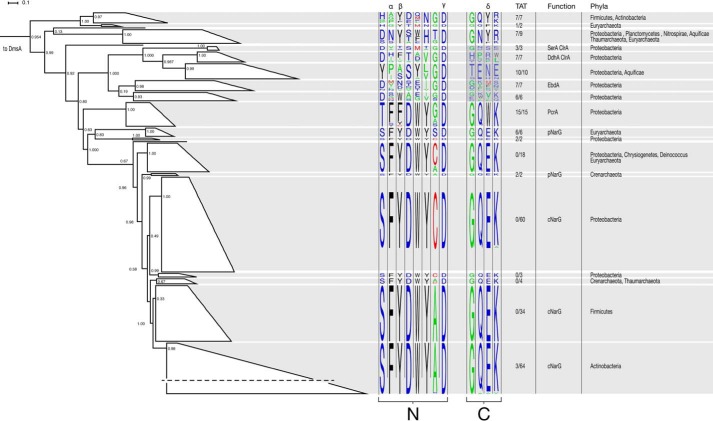
FIGURE 4.
Phylogenetic reconstruction of PcrA and closely related DMSO reductase superfamily enzymes using DmsA and DorA as an outgroup. Active site residues identified from the crystal structure of PcrA were visualized for clades with high bootstrap support using sequence motifs. The positions denoted by α, β, and δ in the sequence alignments correspond to the gate residues relative to the A. suillum PS PcrA. The positions denoted by γ in the sequence alignments correspond to the Asp residue that has been shown or is predicted to bind to the molybdenum atom at the active site of the corresponding enzyme. N and C represent the N- and C-terminal portions of the MBD in each enzyme. The fraction of predicted twin arginine translocation (TAT) signal sequences, physiological function of known members, and taxonomic affiliation are superimposed on the tree. For the clades containing SerA, ClrA, and EbdA, the darker highlighting in the C-terminal portion of the aligned sequences denotes lower confidence in the alignment. SerA is selenate reductase, ClrA is chlorate reductase, EbdA is ethylbenzene dehydrogenase, PcrA is perchlorate reductase, pNarG is periplasmic nitrate reductase, and cNarG is cytoplasmic nitrate reductase. A horizontal dash in the lowermost cNar clade denotes the compression of this large group of sequences into a group suitable for visualization.