Figure.
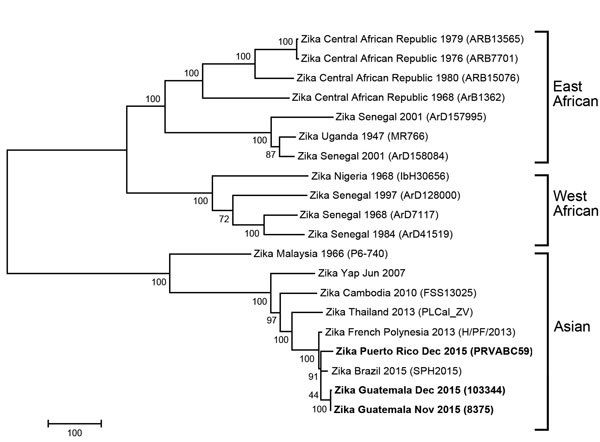
Phylogenetic tree of Zika virus isolates identified from Guatemala and Puerto Rico in December 2015 (indicated in boldface) compared with reference isolates obtained from GenBank. The isolates from Guatemala and Puerto Rico grouped with other Asian genotype viruses. The tree was derived by neighbor-joining methods (bootstrapped 1,000 times) using complete-genome sequences. Location, year identified, and GenBank strain identification for the viruses used in tree construction are shown. Scale bar indicates number of nucleotide substitutions per site. GenBank accession nos.: KU321639 (Brazil 2015 SPH2015), KJ776791 (French Polynesia H/PF/2013), KF383115 (Central African Republic ARB1362), KF383116 (Senegal 1968 ArD7117), KF383117 (Senegal 1997 ArD128000), KF383118 (Senegal 2001 ArD157995), KF383119 (Senegal 2001 ArD158084), KF268948 (CAR 1979 ARB13565), KF268949 (CAR 1980 ARB15076), KF268950 (CAR 1976 ARB7701), EU545988 (Yap 2007), KF993678 (Thailand 2013 PLCal_ZV), JN860885 (Cambodia 2010 FSS13025), HQ234499 (Malaysia 1966 P6-740), HQ234501 (Senegal 1984 ArD41519), HQ234500 (Nigeria 1968 IbH 30656), LC002520 (Uganda 1947 MR766), KU501215 (Puerto Rico PRVABC59), KU501216 (Guatemala 8375), and KU501217 (Guatemala 103344).
