Abstract
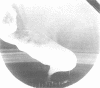
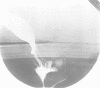
OBJECTIVE--To study the disturbed anorectal physiology associated with constipation in multiple sclerosis. METHODS--Anorectal function in 10 patients with clinically definite multiple sclerosis and constipation has been compared with 10 normal persons and 11 patients with idiopathic constipation, without multiple sclerosis. RESULTS--All 10 constipated patients with multiple sclerosis had difficulty evacuating barium paste during defaecography. In four of these there was complete failure of puborectalis relaxation when straining to defaecate, and in another four there was incomplete puborectalis relaxation. There was no evidence of lower motor neuron involvement of pelvic floor muscles in the multiple sclerosis group. CONCLUSIONS--Paradoxical puborectalis contraction is common in patients with multiple sclerosis in whom constipation is a symptom. This may be a feature of the disturbed voluntary sphincter control mechanism, analogous to detrusor sphincter dyssnergia in the bladder.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleijenberg G., Kuijpers H. C. Treatment of the spastic pelvic floor syndrome with biofeedback. Dis Colon Rectum. 1987 Feb;30(2):108–111. doi: 10.1007/BF02554946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL A. M., FRANKEL H., GUTTMANN L. THE MOTILITY OF THE PELVIC COLON FOLLOWING COMPLETE LESIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD. Paraplegia. 1963 Sep;1:98–115. doi: 10.1038/sc.1963.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruana B. J., Wald A., Hinds J. P., Eidelman B. H. Anorectal sensory and motor function in neurogenic fecal incontinence. Comparison between multiple sclerosis and diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology. 1991 Feb;100(2):465–470. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia Y. W., Fowler C. J., Kamm M. A., Henry M. M., Lemieux M. C., Swash M. Prevalence of bowel dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis and bladder dysfunction. J Neurol. 1995 Jan;242(2):105–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00887825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill K. P., Chia Y. W., Henry M. M., Shorvon P. J. Defecography in multiple sclerosis patients with severe constipation. Radiology. 1994 May;191(2):553–556. doi: 10.1148/radiology.191.2.8153339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick M. E., Meshkinpour H., Haldeman S., Bhatia N. N., Bradley W. E. Colonic dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 1982 Nov;83(5):1002–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick M. E., Meshkinpour H., Haldeman S., Hoehler F., Downey N., Bradley W. E. Colonic dysfunction in patients with thoracic spinal cord injury. Gastroenterology. 1984 Feb;86(2):287–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallan R. I., Williams N. S., Melling J., Waldron D. J., Womack N. R., Morrison J. F. Treatment of anismus in intractable constipation with botulinum A toxin. Lancet. 1988 Sep 24;2(8613):714–717. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry M. M., Snooks S. J., Barnes P. R., Swash M. Investigation of disorders of the anorectum and colon. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1985 Nov;67(6):355–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds J. P., Eidelman B. H., Wald A. Prevalence of bowel dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. A population survey. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jun;98(6):1538–1542. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91087-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton J. M., Lennard-Jones J. E., Young A. C. A ne method for studying gut transit times using radioopaque markers. Gut. 1969 Oct;10(10):842–847. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.10.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm M. A., Hawley P. R., Lennard-Jones J. E. Lateral division of the puborectalis muscle in the management of severe constipation. Br J Surg. 1988 Jul;75(7):661–663. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiff E. S., Swash M. Slowed conduction in the pudendal nerves in idiopathic (neurogenic) faecal incontinence. Br J Surg. 1984 Aug;71(8):614–616. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers H. C., Bleijenberg G. The spastic pelvic floor syndrome. A cause of constipation. Dis Colon Rectum. 1985 Sep;28(9):669–672. doi: 10.1007/BF02553449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. The Disability Status Scale for multiple sclerosis: apologia pro DSS sua. Neurology. 1989 Feb;39(2 Pt 1):291–302. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathers S. E., Ingram D. A., Swash M. Electrophysiology of motor pathways for sphincter control in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Nov;53(11):955–960. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.11.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathers S. E., Kempster P. A., Law P. J., Frankel J. P., Bartram C. I., Lees A. J., Stern G. M., Swash M. Anal sphincter dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1989 Oct;46(10):1061–1064. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520460037010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen T., Pedersen E. Neurourodynamic evaluation of voiding dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1984 Jun;69(6):402–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1984.tb07823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston D. M., Lennard-Jones J. E. Anismus in chronic constipation. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 May;30(5):413–418. doi: 10.1007/BF01318172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorvon P. J., McHugh S., Diamant N. E., Somers S., Stevenson G. W. Defecography in normal volunteers: results and implications. Gut. 1989 Dec;30(12):1737–1749. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.12.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S. N., Ebers G. C. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 1983 Jun;84(6):1640–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull G. K., Bartram C. I., Lennard-Jones J. E. Radiologic studies of rectal evacuation in adults with idiopathic constipation. Dis Colon Rectum. 1988 Mar;31(3):190–197. doi: 10.1007/BF02552545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull G. K., Lennard-Jones J. E., Bartram C. I. Failure of rectal expulsion as a cause of constipation: why fibre and laxatives sometimes fail. Lancet. 1986 Apr 5;1(8484):767–769. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91783-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Grise P., Roquebert M., Hellot M. F., Mihout B., Samson M., Beuret-Blanquart F., Pasquis P., Denis P. Radiopaque markers transit and anorectal manometry in 16 patients with multiple sclerosis and urinary bladder dysfunction. Dis Colon Rectum. 1987 Feb;30(2):95–100. doi: 10.1007/BF02554940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]