Fig. 6.
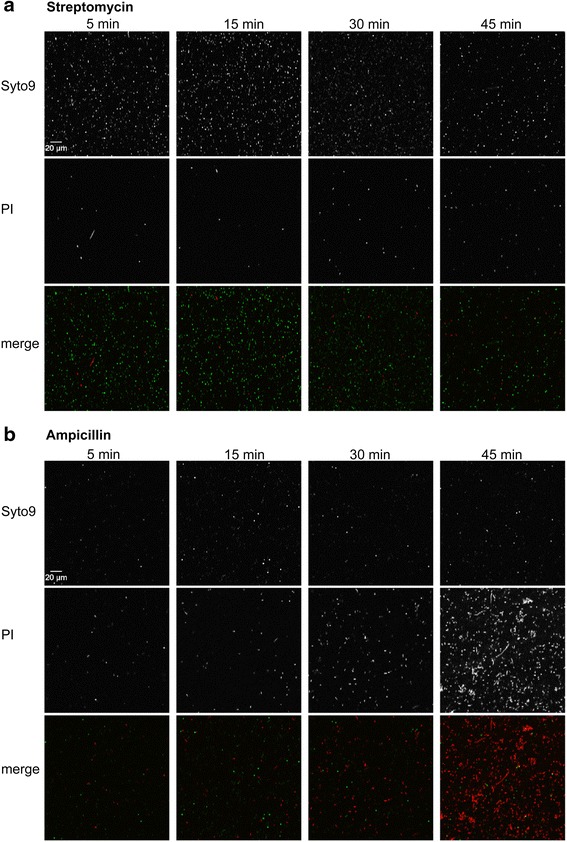
Cell wall permeability of E. coli after antibiotic treatment investigated by fluorescence microscopy. Fluorescence microscopy of E. coli cultures incubated with streptomycin a and ampicillin b for 5, 15, 30 and 45 min and stained with SYTO9 and propidium iodide (PI). SYTO9 is membrane permeant and generally labels all bacteria in a population with a green fluorescence. PI is characterized by its red fluorescence and replaces the green fluorescence in cells with reduced membrane impermeability. Images after ampicillin treatment showed increased signs of cell debris in the red fluorescence channel at 30 and 45 min time point compared to samples after streptomycin treatment
