Fig. 4.
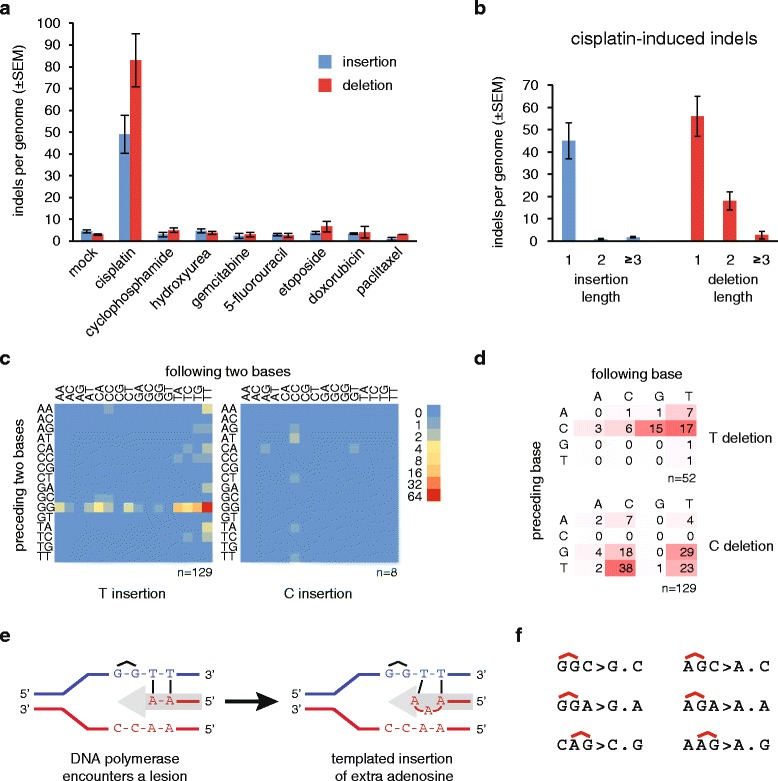
Cisplatin-induced insertions and deletions. a The mean number of observed insertions (blue) and deletions (red) per genome following the described treatment regimen with the indicated drugs. Error bars indicate SEM. b Length distribution of cisplatin-induced insertions and deletions. c Heat map of the frequency of one-base insertions, classified according to the preceding and the following two bases as indicated. The inserted base is shown below each panel. The equivalent mutations on the two strands are added and shown as T or C insertions. d Table and heat map of the frequency of one-base deletions, classified according to the preceding and the following base as indicated. The equivalent mutations on the two strands are added and shown as T or C deletions, shown to the right. e A schematic model of the generation of the most common GGTT > GGTTT insertions during DNA replication. The incoming DNA polymerase (grey arrow) inserts adenosines opposite the thymine bases, then it inserts an extra adenosine upon encountering the cisplatin-induced GG intrastrand crosslink. f Sequence context of the most common one-base deletions shown on the purine rich strand, with the position of putative intrastrand crosslinks indicated above the sequence
