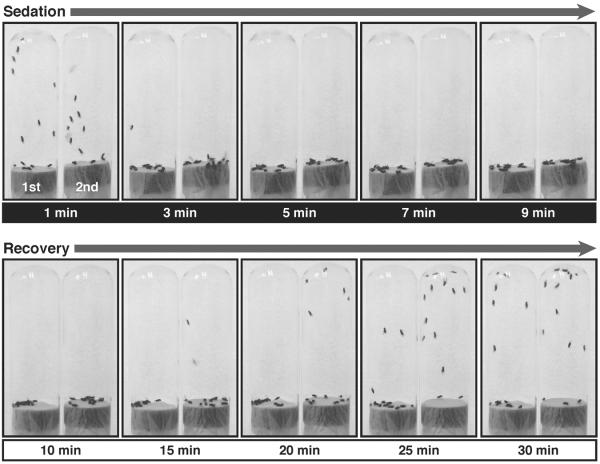
Figure 2. Benzyl alcohol tolerance assay.
Shown are sequential pictures of two vials of flies taken at different time points of sedation and recovery from 0.4 % benzyl alcohol exposure. The vial on the left in every picture contains naïve flies, which have never been treated before; this is their first exposure (1st). The vial on the right contains flies that were previously sedated (24 hours earlier) with a similar dose of benzyl alcohol; this is their second exposure (2nd). The time point at which each picture was taken is indicated under each picture in minutes after start of the treatment. Time points from 1 to 9 minutes (white text over black) are in the presence of the solvent. The solvent has been removed at 10 minutes. Time points from 10 to 30 minutes (black text over white) are during the recovery in a solvent-free tube. Although both groups knock down simultaneously, flies recovering from the 2nd sedation recover negative geotaxis at earlier time points than flies recovering from their 1st sedation do.