FIG 1.
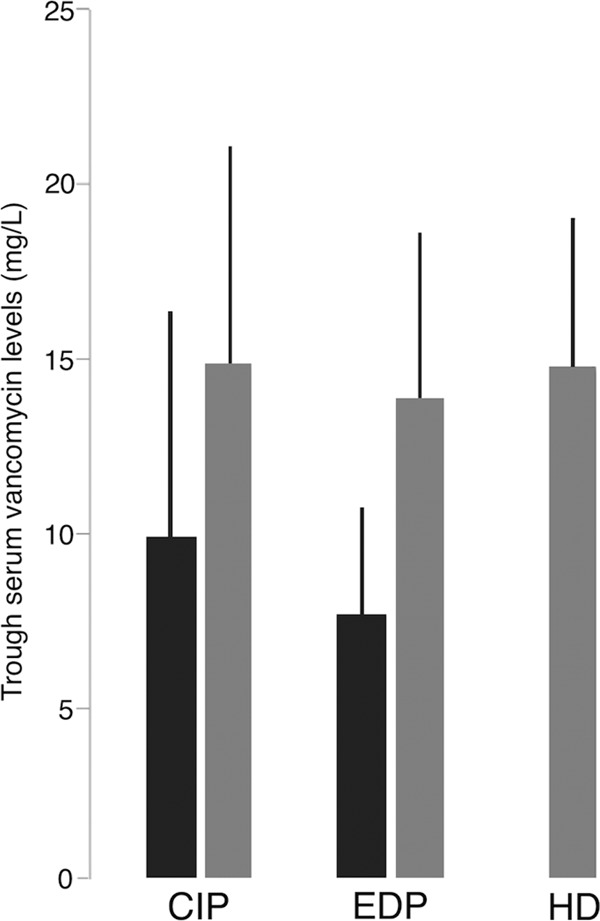
Recommendations of a vancomycin loading dose (LD), to achieve early therapeutic levels, have been established after several studies evaluating trough serum vancomycin concentrations after an LD. In critically ill patients (CIP), trough vancomycin levels (mean ± SD) after a fixed LD of 2 g (≈30 mg/kg, n = 21 patients) was higher than in patients without an LD (n = 31) (P = 0.01) in an intervention observational study (31) (evidence level IIB [83]). In patients presenting to an emergency department (EDP), trough levels (mean ± SD) after an LD of 30 mg/kg (n = 50) were higher than without an LD (n = 49) (P < 0.001) in a randomized clinical trial (30) (evidence level IA [83]). Finally, in patients on hemodialysis (HD) (n = 15), trough serum levels (mean ± SD) after an LD of 20 mg/kg (32) were similar to those found in the above-mentioned two studies carried out in patients with normal renal function (evidence level IIC [83]).
