FIG 1.
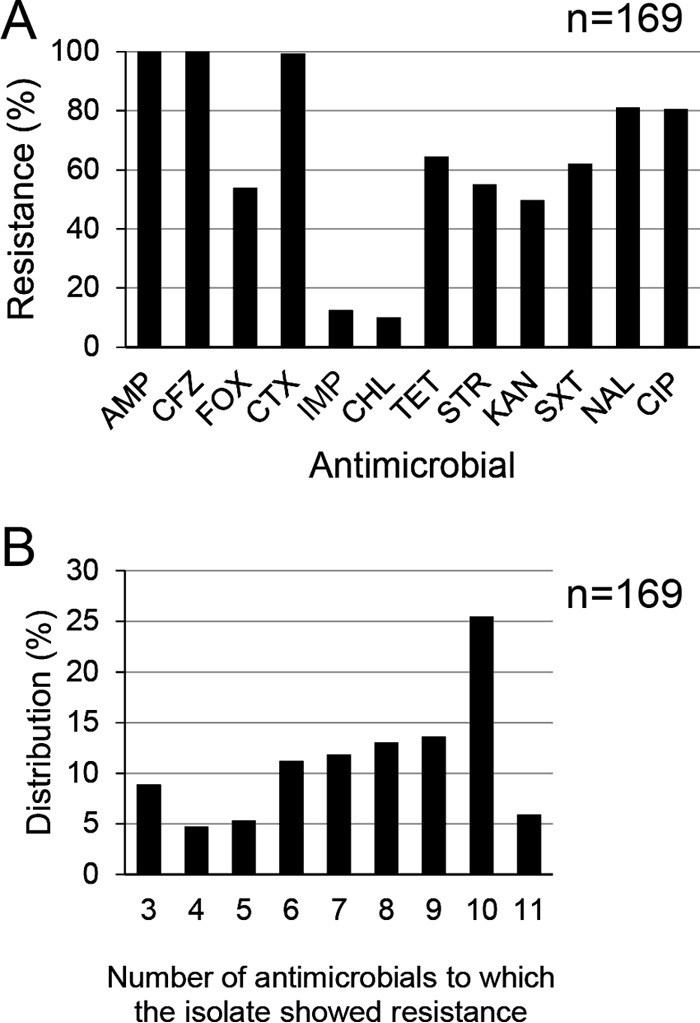
(A) Distribution of resistance to 12 antimicrobials among the extended-spectrum-cephalosporin-resistant and/or carbapenem-resistant E. coli isolates. The x axis indicates the antimicrobials used in this study: ampicillin (AMP), cefazolin (CFZ), cefoxitin (FOX), cefotaxime (CTX), imipenem (IMP), chloramphenicol (CHL), tetracycline (TET), streptomycin (STR), kanamycin (KAN), sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (SXT), nalidixic acid (NAL), and ciprofloxacin (CIP). The y axis indicates the prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant isolates. (B) The numbers of antimicrobials to which the same E. coli isolates for which the results are shown in panel A are resistant.
