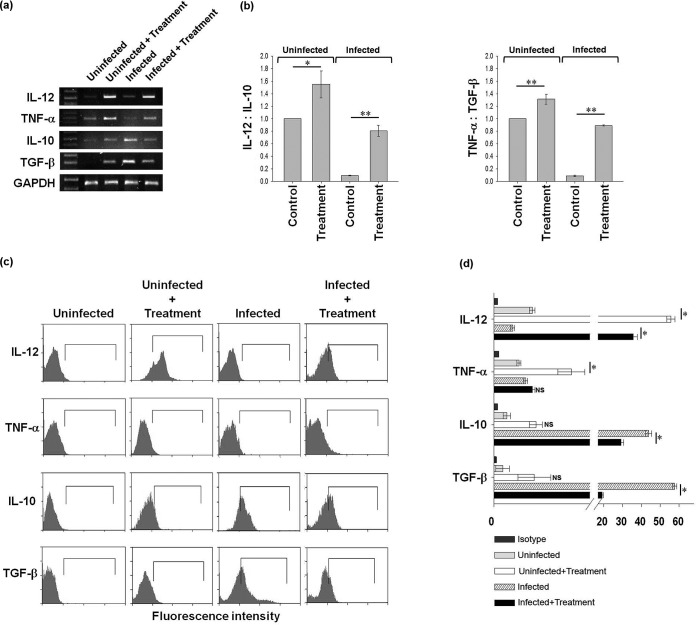
FIG 2.
Astrakurkurone could upregulate the release of proinflammatory cytokines in L. donovani-infected macrophages in vitro. (a) Astrakurkurone induced the release of proinflammatory cytokines and prevented the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines in L. donovani-infected macrophages at the mRNA level as measured by semiquantitative reverse transcriptase PCR. Data are representative of results of 5 independent experiments. (b) The densitometry ratio of mRNA expression of proinflammatory to anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-12:IL-10 and TNF-α:TGF-β) was higher in both uninfected and infected macrophages, which indicated the induction of the Th1 response in vitro (*, P < 0.002; **, P < 0.001). (c) A significant induction of IL-12 in L. donovani-infected macrophages and the simultaneous downregulation of both IL-10 and TGF-β, the anti-inflammatory arms, led to effective control of Leishmania infection in macrophages at 48 h in vitro. Data are representative of results of 5 independent experiments. (d) The statistical significance of the induction of proinflammatory cytokines, as estimated by flow cytometry (*, P < 0.001; NS, nonsignificant).