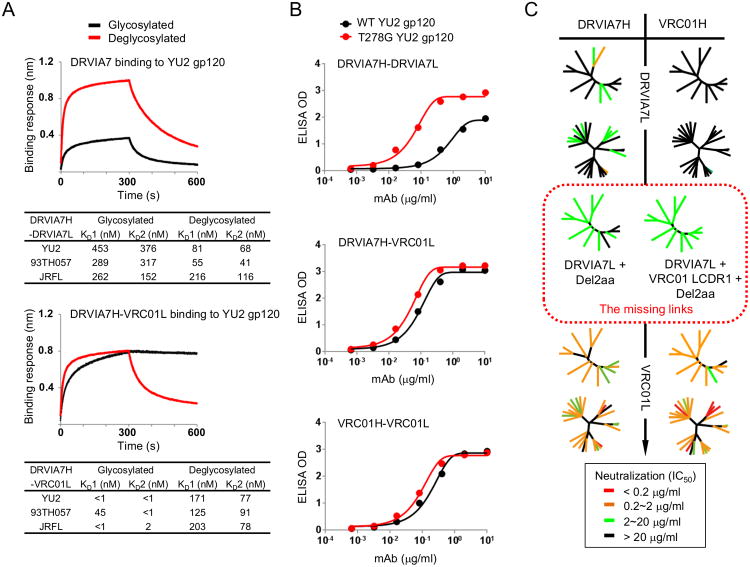
Figure 3. Interaction between DRVIA7 light chain and the N276 glycan determines the neutralizing breadth of the antibody.
(A) Octet association and dissociation curves for DRVIA7 or DRVIA7H-VRC01L towards glycosylated or endoH deglycosylated gp120 YU2 at 1000 nM concentration (above). Binding response (nm shift) is plotted as a function of time (s), with KD values indicated below. (B). ELISA binding for DRVIA7, DRVIA7H-VRC01L and VRC01 against YU2 gp120 (black) and T278G (i.e. no glycan at N276) YU2 gp120 (red), with the optical density (OD) plotted as a function of antibody dilution (μg/ml). (C) The neutralizing activity of DRVIA7, VRC01H-DRVIA7L, DRVIA7H-VRC01L and VRC01 against both the global and DRVI panels of pseudoviruses. In addition, the neutralizing activity of two DRVIA7 variants (circled by red dotted lines), DRVIA7H-DRVIA7L + Del2aa and DRVIA7H-DRVIA7L + VRC01 LCDR1 + Del2aa, against the global panel is shown. Neutralization potencies (Tables S4A-B) are mapped onto dendrogram representations of the virus panels as in Figure 1. See also Figure S3.