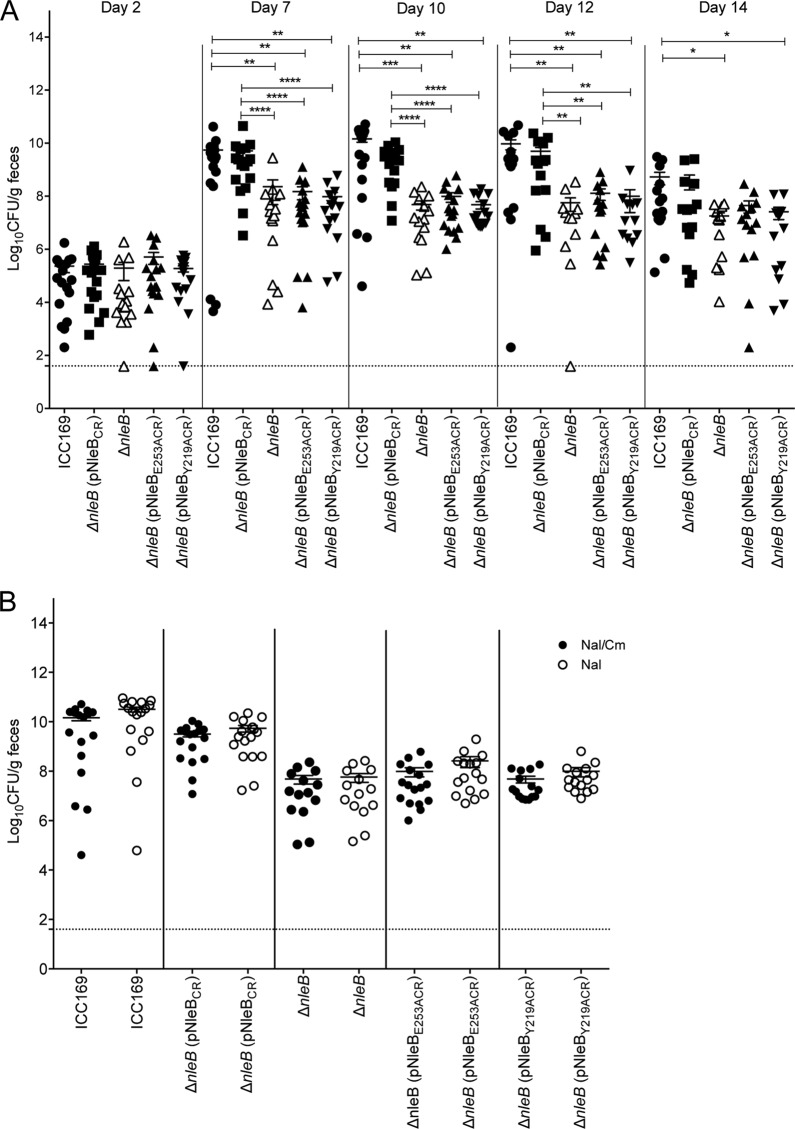
FIG 5.
Residues Y219 and E253 in Citrobacter rodentium NleB are important for intestinal colonization. (A) Colonization of C57BL/6 mice with the indicated C. rodentium derivatives. Each data point represents the log10 number of CFU per gram of feces per individual animal on days 2, 7, 10, 12, and 14 postinfection. Means ± SEMs are indicated. Dotted line, detection limit. Significant differences were determined by the Mann-Whitney U test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (B) Comparison of viable counts of C. rodentium derivatives from fecal samples collected on day 10 postinfection on LA supplemented with nalidixic acid (Nal) and chloramphenicol (Cm) versus LA supplemented with nalidixic acid only to determine the extent of pACYC loss in vivo.