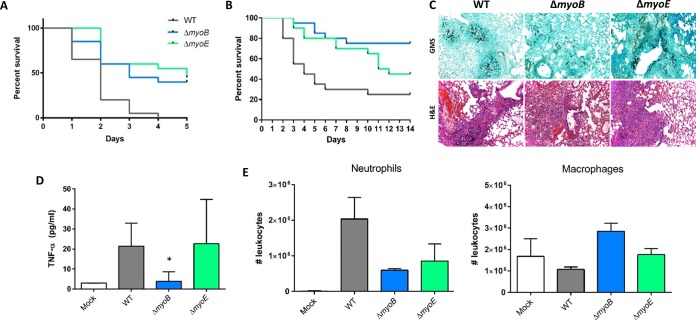
FIG 4.
Effects of myoB and myoE deletion on virulence in the invertebrate host, G. mellonella, and in a murine model of invasive aspergillosis. (A) Conidia (5 × 106) were inoculated into an invertebrate host, G. mellonella larvae, and survival was scored every 24 h for 5 days. (B) Effect of myoB or myoE deletion on virulence in a persistently immunosuppressed murine model. Mice were immunosuppressed with cyclophosphamide and triamcinolone acetonide prior to infection. Conidia (4 × 106) were inoculated into the mice intranasally, and survival was scored every 24 h for 14 days. (C) Histopathological examination of the murine lungs 3 days after infection showed little fungal burden in the ΔmyoB strain, while the wild-type and ΔmyoE strains showed similar fungal burdens by Gomori methenamine silver stain (GMS). Inflammation was similar in the wild-type and single-deletion strains by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). (D) BALF from infected mice was used to determine TNF-α release using ELISA. Mice infected with the ΔmyoB strain released significantly less TNF-α than the wild-type or ΔmyoE strain. (E) BALF from infected mice was used for leukocyte analysis by flow cytometry. *, P < 0.05 using an unpaired t test (compared to the WT). The error bars indicate standard errors of the means.