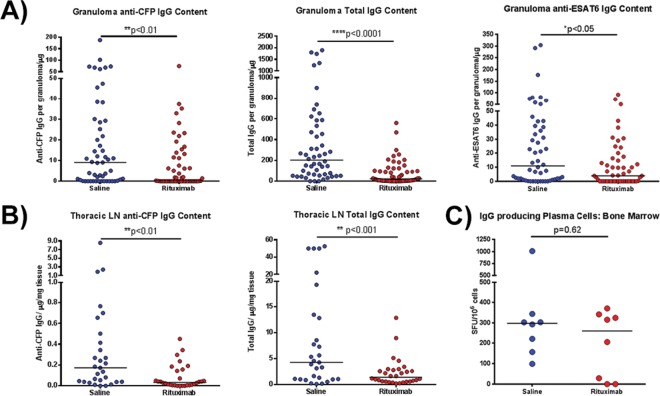
FIG 2.
Assessment of antibody profile of granuloma homogenates after rituximab treatment. (A) Granuloma homogenates obtained at necropsy were assayed for the amount of CFP-specific IgG, ESAT6-specific IgG, or total IgG present using ELISA. Antigen-specific IgG levels were significantly reduced after rituximab treatment compared to saline controls (the median granuloma antibody content was reduced ∼10-fold in the case of CFP and 5-fold for ESAT6). The total IgG content within rituximab-treated granulomas was also reduced by ∼10-fold. Each point represents one granuloma (n = 16 animals, n = 110 granulomas, ∼6 granulomas per animal). (B) Homogenates from lymph node samples were assayed for the amount of CFP-specific IgG and total IgG present. Both antigen specific IgG and total IgG were reduced with rituximab by approximately 2- to 5-fold. Each point represents one thoracic LN sample (n = 16 animals, n = 59 thoracic LN samples, ∼3 thoracic LN samples per animal). (C) The number of plasma cells generating IgG within the bone marrow, assayed by a plasma cell ELISPOT assay, were similar within both groups. Each point presents one animal (n = 16 animals, ∼8 animals per group). All statistical P values were obtained using the Mann-Whitney test unless otherwise stated.