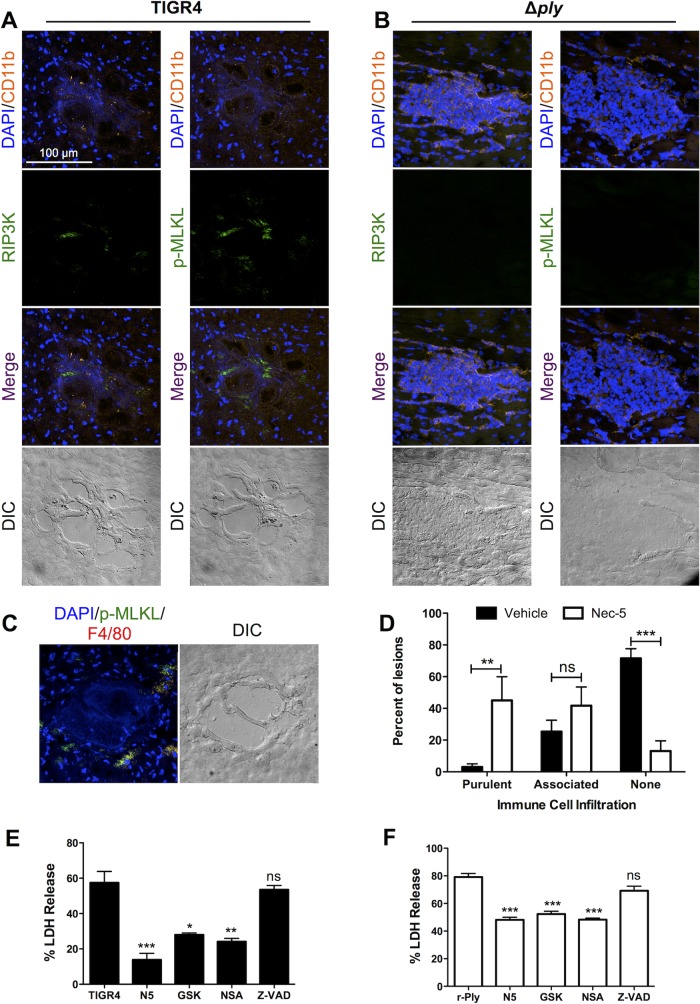
FIG 7.
Infiltrated immune cells die due partially to necroptosis. (A to C) Representative IFM images of stained serial frozen sections from mice challenged with TIGR4 (A) and TIGR4 Δply (B) costained for DAPI, CD11b, and either p-MLKL or RIP3 kinase or mice challenged with TIGR4 costained for DAPI, p-MLKL, and F4/80 (C). Magnification, ×40 with a zoom factor of 1.0. (D) Percentage of microlesions from each mouse that either were fully purulent, contained peripherally associated immune cells, or were completely devoid of immune cells (as determined at a ×25 magnification) following infection of mice with TIGR4 and treatment of mice with necrostatin-5 (Nec-5) or the vehicle as a control. THP-1 macrophages were pretreated with necrostatin-5 (N5), GSK'872 (GSK), necrosulfonamide (NSA), or Z-VAD-FMK (Z-VAD) and challenged with either TIGR4 (E) or recombinant pneumolysin (r-Ply) (F). For panels E and F, cell death was measured by determination of the amount of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the supernatants, *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ns, not significant.