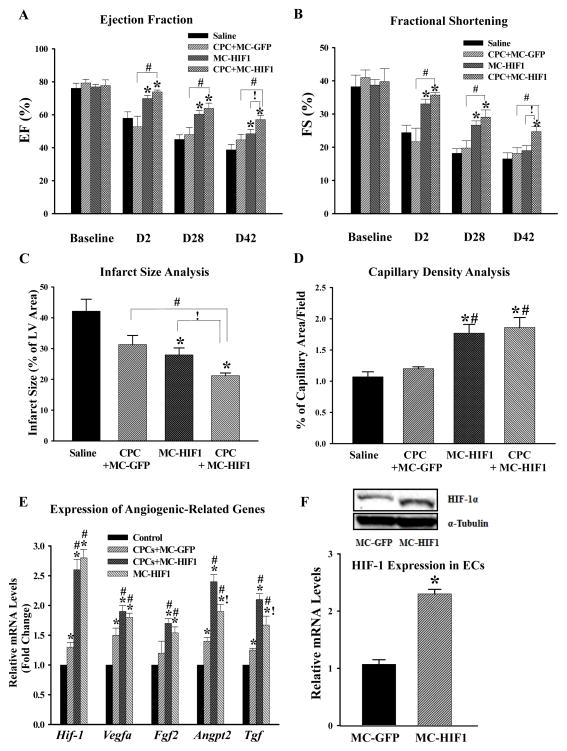
Figure 2.
Combination of cell and gene therapy provides synergistic therapeutic effects following MI. Comparison of (A) ejection fraction and (B) fractional shortening among all 4 groups at indicated time points revealed that CPCs co-delivered with MC-HIF1 had superior therapeutic effects among all groups. *P<0.05 vs. saline group; #P<0.05 vs. CPCs + MC-GFP; !P<0.05 vs. MC-HIF1 (N=10/group). (C) Three days post-MI, mice from each group were sacrificed and hearts were collected for determination of infarct size by tetrazolium chloride staining. *P<0.05 vs. saline group; #P<0.05 vs. CPCs + MC-GFP; !P<0.05 vs. MC-HIF1 (N=6/group). (D) Vascular density in each group was determined by CD31 staining at 7 days post-MI. *P<0.05 vs. saline group; #P<0.05 vs. CPCs + MC-GFP (N=6/group). (E) Areas close to engrafted GFP+ CPCs were laser microdissected to assess levels of angiogenic gene activation. Samples were collected 5 days post-MI. qPCR showed that MC-HIF1 upregulates the expression of angiogenic genes, some of which were further augmented with the presence of CPCs. *P<0.05 vs. control (non-ischemic remote zone of MC-HIF1); #P<0.05 vs. CPCs + MC-GFP; !P<0.05 vs. CPCs + MC-HIF1 (N=5/group). (F) In a separate set of experiments, mice subjected to MI received either MC-GFP or MC-HIF1 only. Three days later, cardiac ECs were isolated from the peri-infarct region, ECs from MC-HIF1 group were found to have higher expression of HIF-1 at both protein (upper panel) and gene levels (lower panel) compared to ECs from MC-GFP group, indicating that cardiac ECs are receptive to MC-HIF1 transfection. *P<0.05 vs. MC-GFP (N=6/group).