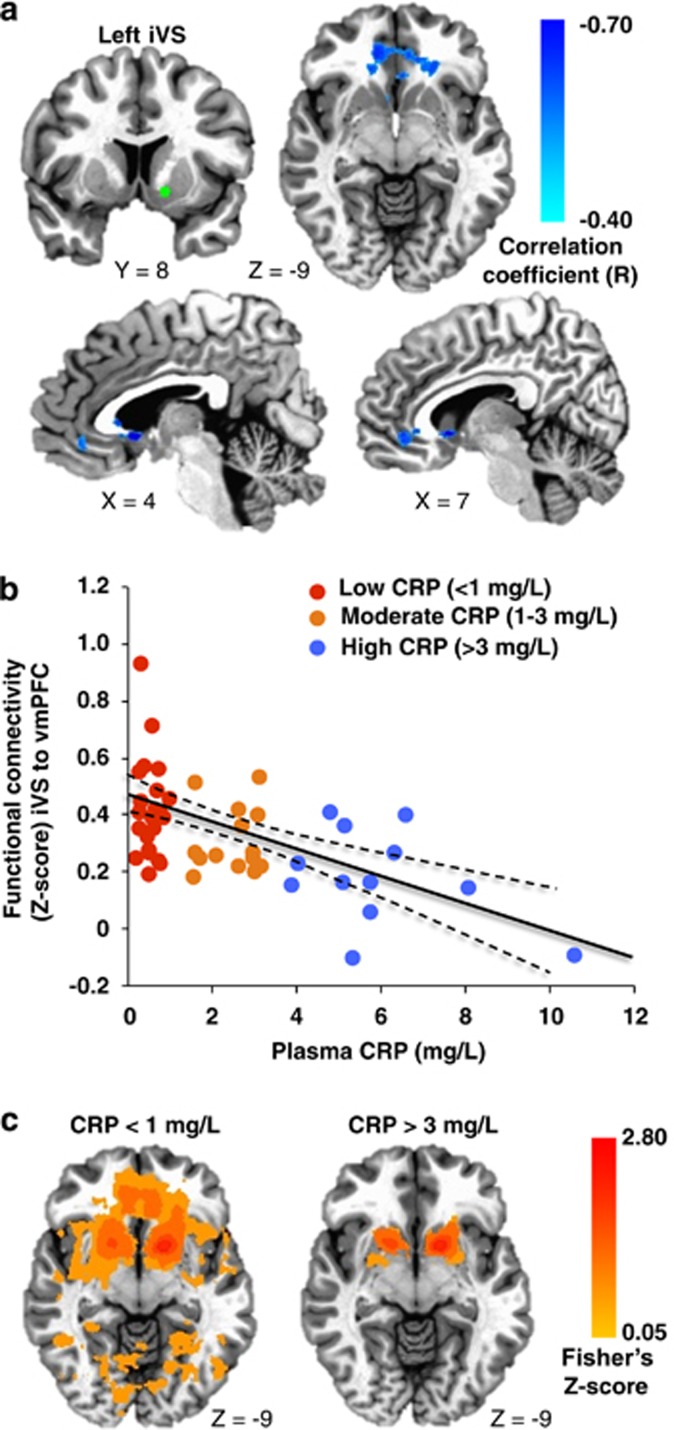
Figure 1.
Plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) was negatively associated with functional connectivity between left inferior ventral striatum (iVS) (green seed) and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC; BA32, x=−2, y=33, z=−6), with increasing CRP predicting decreasing connectivity (cyan-blue intensity, R=−0.40 to −0.70) in patients with depression (a and b). Z-score maps demonstrated that, whereas patients with high inflammation (CRP>3 mg l−1) exhibited no significant connectivity between left iVS and vmPFC, the subjects with low inflammation (CRP<1 mg l−1) exhibited robust positive connectivity (yellow-red intensity) between these brain regions (c). Clusters are overlaid onto canonical structural brain images in the axial (z=−9: a and c) and sagittal (x=4 and 7: a) planes, corrected P<0.05.