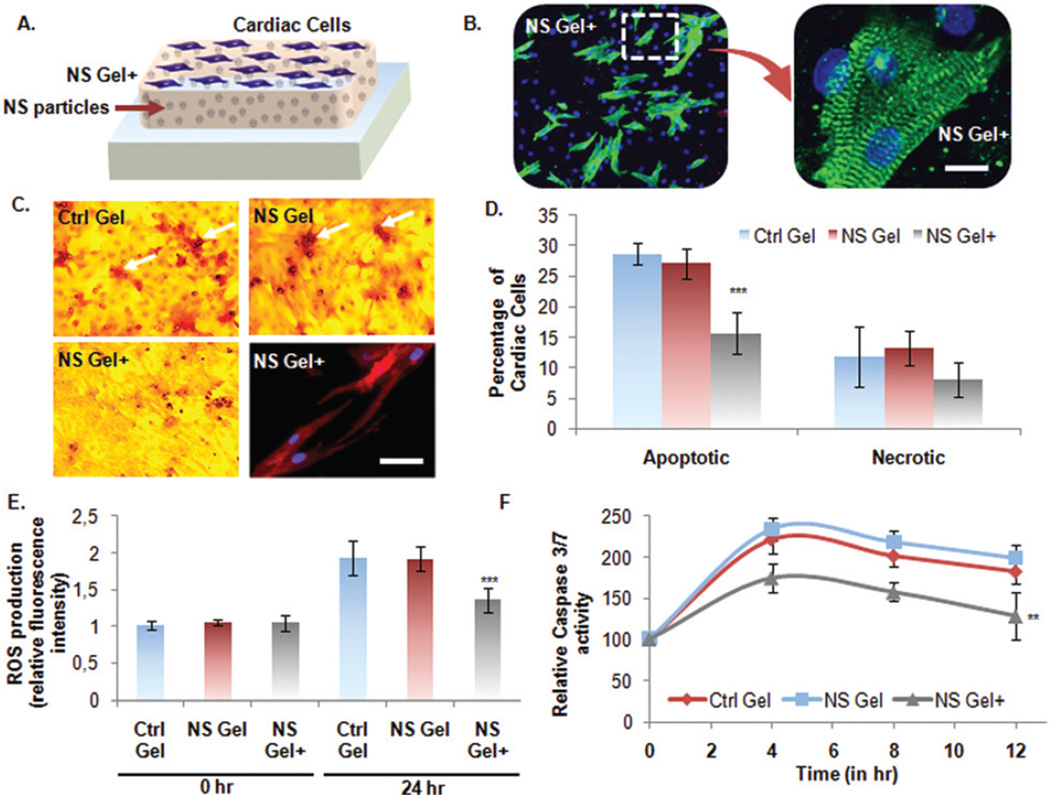
Fig. 4.
Cardioprotective nature of the developed bioactive nanocomposite hydrogel. (A) Schematic of culturing neonatal CMs on nanocomposite hydrogels. (B) Fluorescence microscope images of CMs grown in standard condition on NS+ hydrogel. The cells were immunostained with cardiac specific marker, sarcomeric α-actinin, and nuclei with DAPI (Scale bar: 10 µm). (C and D) Apoptosis assay on CMs under stressed condition by Deadend Colorimetric TUNEL assay. (Scale: bar: 50 µm). Number of apoptotic cells per well was quantified and represented in graph as percentage apoptotic cells per group. MTS assay was also performed to quantify the percentage of necrotic cells. The picture on lower right panel shows CM cells grown on the NS+ hydrogel under the above mentioned stressed condition still retained expression of intact cardiac marker, sarcomeric α-actinin. (E) Detection of ROS-induced apoptosis. Intracellular ROS quantified in terms of relative fluorescence intensities normalized to Ctrl gel value at 0 h. (F and G) To investigate the anti-apoptotic effects of the NS+ hydrogel, Caspase-3/7 activity was measured as an early indicator of apoptosis using Apo-ONE® homogeneous caspase-3/7 assay Kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Data are expressed as mean value ± Standard Deviation (SD). *** = P < 0.001 and ** = P < 0.01 compared to Control Gel, n = 3.