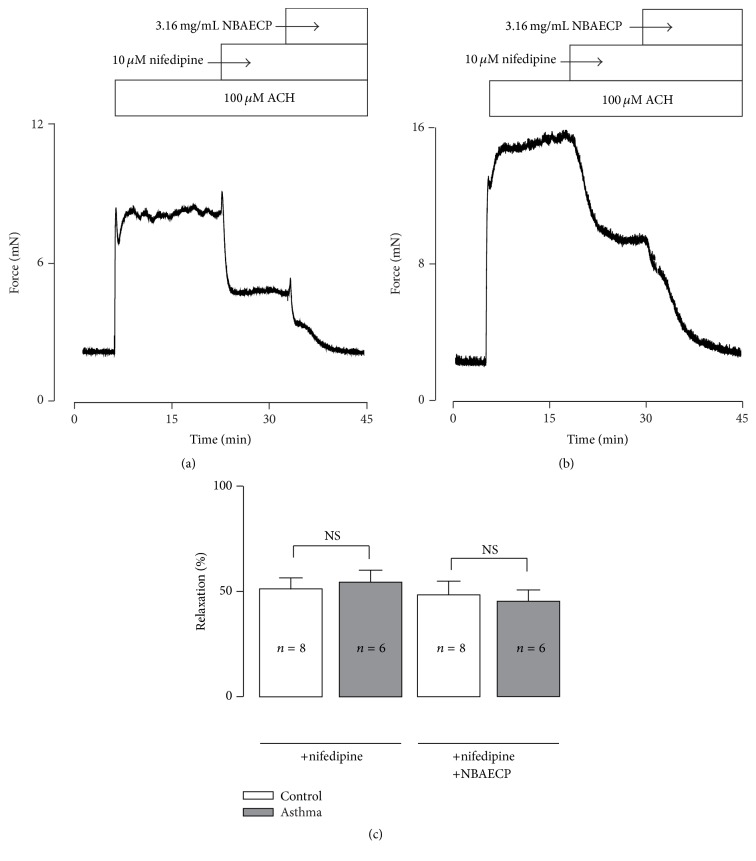
Figure 3.
Nifedipine partially inhibits ACH-caused contraction. (a) ACH (100 μM) induced a sustained contraction in a control TR, which was partially inhibited by nifedipine (10 μM). The remaining contract was further blocked by NBAECP (3.16 mg/mL). (b) An identical experiment was performed in an asthmatic TR. (c) The summary data from 8 control and 6 asthmatic TRs. NS P > 0.05. These data demonstrated that activation of L-type Ca2+ channels played a role in ACH-induced contraction, and NBAECP could inhibit nifedipine-resistant channels, resulting in total relaxation.