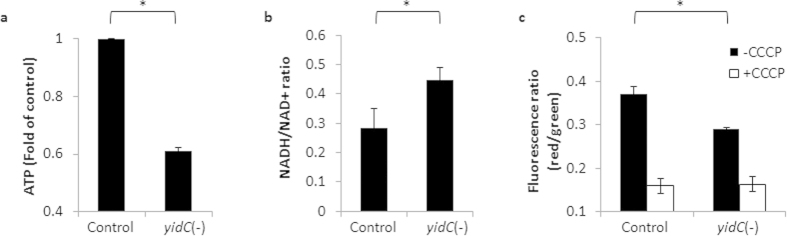
Figure 4. Effect of YidC depletion on cellular redox balance.
(a–c) Effect of YidC depletion on cellular ATP levels (a), NADH/NAD+ ratio (b) and membrane potential (c), relative to control Mtb. Both the control and yidC(−) strains of Mtb cultured for 4 days in 7H9-OADS medium containing 50 ng/ml ATc were used. ATP was measured as described in Methods. For estimating NADH/NAD+ ratios, cell extracts were prepared by heat lysing cells at 55 °C for 10 minutes either in 0.2 M HCl (For NAD+ extraction) or 0.2 M NaOH (For NADH extraction). NADH and NAD+ levels were measured using yeast alcohol dehydrogenase typically as described earlier53. Membrane potential was determined using BacLight Bacterial Membrane Potential Kit (Molecular Probes) with 1 ml bacterial cultures at OD600 of 1.0 in the absence or the presence of ionophore CCCP. Briefly, cells were incubated with 30 μM of carbocyanine dye 3,3′-diethyloxacarbocyanine iodide (DiOC2) with or without 5 μM CCCP. Stained cells were analyzed using 488-nm excitation and emission at 528-nm (green) and 620-nm (red), respectively. The DiOC2 red:green ratios were calculated using mean fluorescence intensities that provide a measure of membrane potential. Mean ± s.d. of three experiments is shown in (a–c). Asterisks describe levels of significance (P < 0.05).