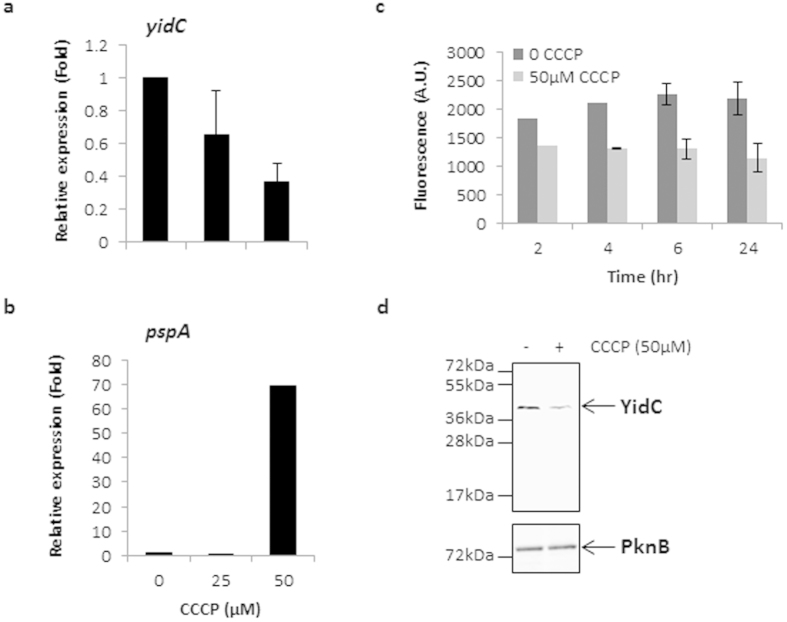
Figure 7. Effect of membrane potential on expression of YidC.
(a,b) qRT-PCR studies were performed to assess the effect of ionophore CCCP on the expression of yidC (a) and a control gene pspA, which is induced by CCCP treatment44 (b). Briefly, Mtb cultures were incubated with 25 and 50 μM CCCP for 2 hours followed by RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis. Equal amounts of cDNAs were subsequently used for qRT-PCR by amplifying ~200 bp region of respective ORFs using specific forward and reverse primers (Supplementary Table 2). Data were obtained after normalization to sigA transcript levels, which remained constant in both the CCCP-treated and untreated cultures. Mean ± s.d. of three measurements is shown in (a,b). (c,d) Effect of 50 μM CCCP treatment on YidC expression was also observed either in Mtb expressing YidC-GFP at different time points by estimation of fluorescent intensities (c), or in wild-type bacteria after 6 hours, by anti-YidC immunoblotting of 20 μg proteins from envelope fraction (d). Mean ± s.d. of three measurements is shown in (c); data represent two experiments in (d). Overall, these results demonstrate that expression of YidC is regulated by membrane potential in Mtb.