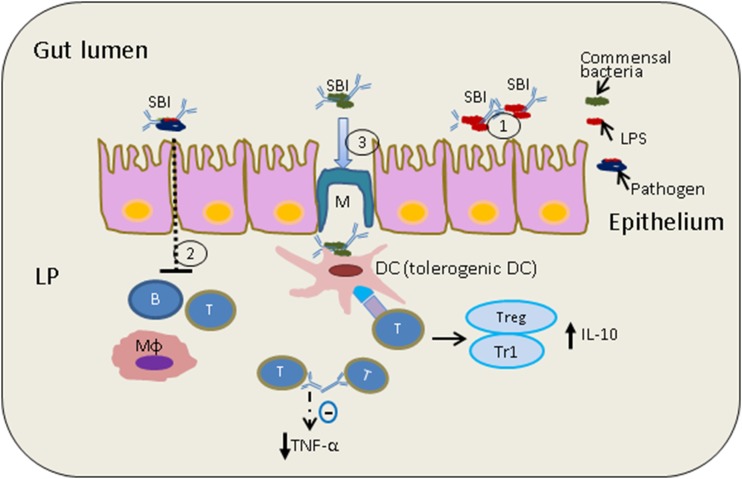
FIGURE 1.
Proposed mechanisms of action of oral Ig SBI. (1) SBI binds luminal bacteria and their endotoxins (LPS), providing a level of immune exclusion. (2) Reduced transepithelial antigen absorption across the small and/or large intestine has been linked to reduced immune activation, including effects on B cells, T cells, and macrophages. (3) SBI may interact with healthy commensals to induce tolerogenic DCs. Shown is a tolerogenic DC signaling to CD4+ helper T cells, which are known to communicate with Treg/Tr1 cells to produce anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Immune homeostasis may reduce production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and would increase production of IL-10. CD4+, cluster of differentiation 4; DC, dendritic cell; LP, lamina propria; SBI, serum-derived bovine Ig; Treg, Foxp3+ regulatory T cell; Tr1, Foxp3− IL10-producing regulatory T cell.