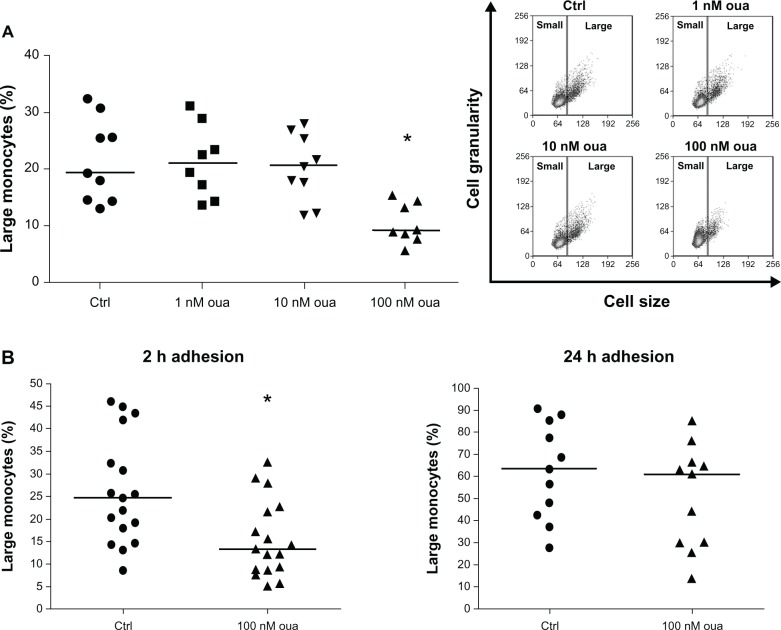
Figure 2.
(A and B) Ouabain (Oua) inhibits the appearance of large monocytes in culture. (A) After 2-hour adhesion, cultures containing peripheral blood mononuclear cells were washed for lymphocyte removal, and monocytes were incubated in the presence or absence of several Oua concentrations for a further 24 hours. Next, the number of large monocytes was determined in each condition, using the control (Ctrl) as a parameter to create gates delimiting small- and large-monocyte subpopulations. inset portrays a representative experiment showing the dot plot of cell size versus cell granularity obtained by flow cytometry. (B) Monocytes were allowed to attach to the substrate for either 2 hours or 24 hours. Then, cultures were washed for lymphocyte removal, and monocytes were incubated for a further 24 hours in the presence or absence of 100 nM Oua. Analysis of large-monocyte percentage was similar to that of Figure 2A.
Notes: Values in A and B refer to the medians of large monocytes; *statistical difference from the respective Ctrl (P < 0.01, Mann–Whitney test).