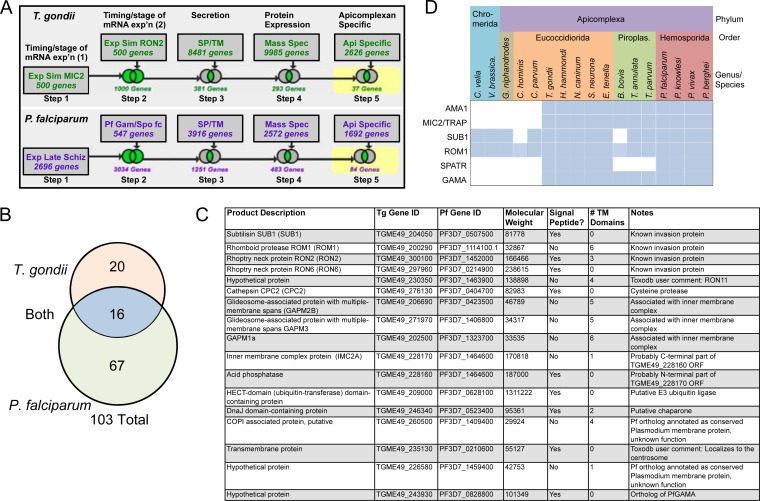
FIG 1 .
Identification of apicomplexan-specific putative invasion proteins. (A) Schematic representation of the search strategies used to find T. gondii (top row) and P. falciparum (bottom row) invasion proteins in the Toxoplasma and Plasmodium genome databases. Exp or exp’n, expression; Sim, simulation; SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane; Spec, spectroscopy; Api, apicomplexan; Schiz, schizont; gam, gametocyte; Spo, sporozoites; fc, fold change. (B) Venn diagram depicting the number of proteins identified exclusively in the T. gondii search (top), in both the T. gondii and P. falciparum searches (middle), and exclusively in the P. falciparum search (bottom). Note that two of the hits (TGME49_228170 and TGME49_22180) identified in both the T. gondii and P. falciparum searches likely correspond to one gene; thus, 16 proteins are depicted in the middle section rather than 17. (C) Features of the hits identified in the T. gondii and P. falciparum searches. (D) Phylogenetic distribution of microneme proteins that are conserved among most apicomplexans.