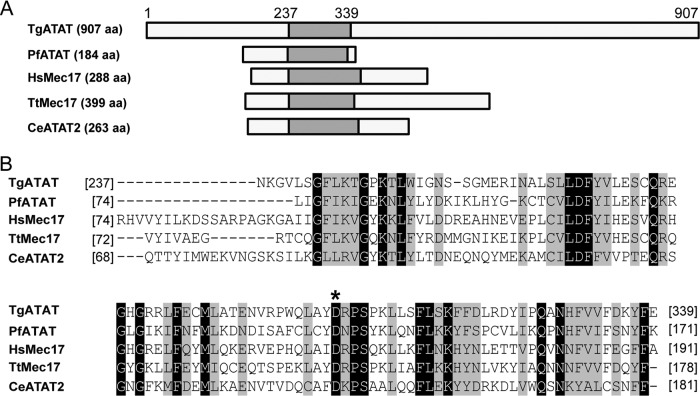
FIG 3 .
Comparison of ATAT/Mec-17 homologues. (A) Depiction of ATAT protein sequences from T. gondii (TgATAT, TGME49_31600), Plasmodium falciparum (PfATAT, PF3D7_0924900), Homo sapiens (HsMec17, XP_005249477.1), Tetrahymena thermophila (TtMec17, TTHERM_00355780), and C. elegans (CeATAT2, CELE_W06B11.1), with the number of amino acids (aa) in parentheses. Gray boxes represent the lysine acetyltransferase domain. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of the KAT domain of the indicated ATAT homologues with identical residues highlighted in black and similar residues highlighted in gray. The asterisk denotes an aspartic acid residue previously shown to be important for ATAT activity (43).