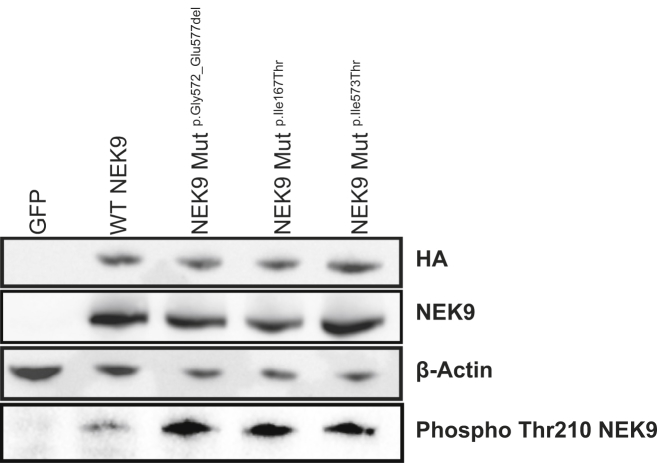
Figure 3.
NEK9 Mutations Cause Increased Phosphorylation of NEK9
HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with GFP as a negative control or HA-tagged NEK9 constructs, including those encoding wild-type (WT) NEK9, p.Gly572_Glu577del NEK9, p.Ile167Thr NEK9, and p.Ile573Thr NEK9. 24 hr post-transfection with lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen), protein lysates were run on SDS-page gels and transferred to nitrocellulose. Blots were probed with 1:1,000 anti-HA (ab18181; Abcam), 1:1,000 anti-beta-actin (A5316; Sigma), 1:10,000 anti-NEK9 (ab138488; Abcam), and 1:250 anti-phospho-NEK9 (ab63553; Abcam). In contrast to expression of wild-type NEK9, expression of each of the three mutant constructs led to increased phosphorylation of NEK9 despite equivalent protein expression detected by blotting for HA, total NEK9, and actin. This experiment was repeated three times, confirming increased phospho-NEK9 in cells expressing mutant alleles.