Figure 1.
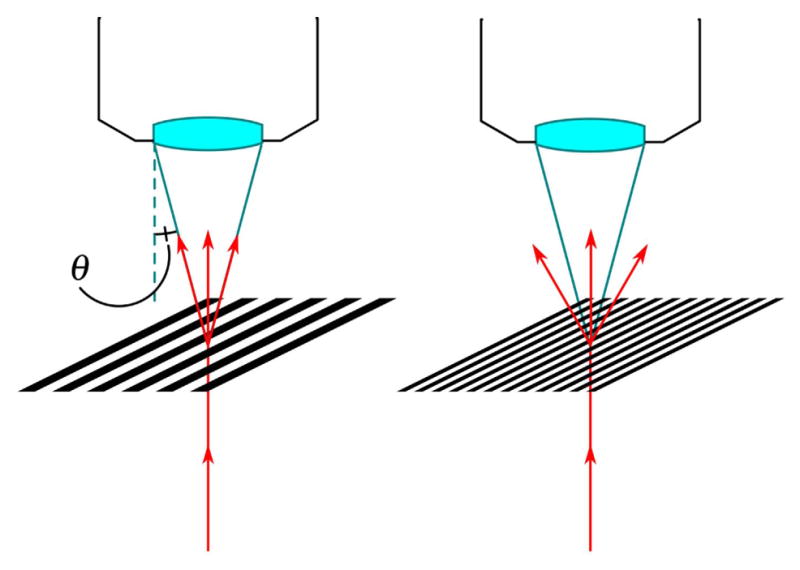
Abbe’s theory of image formation explains how diffracted light from the specimen is collected by an objective lens. Light diffracted at a larger angle than the acceptance angle (θ) of the objective is lost and, thus, so is the spatial information associated with it.
