FIGURE 1.
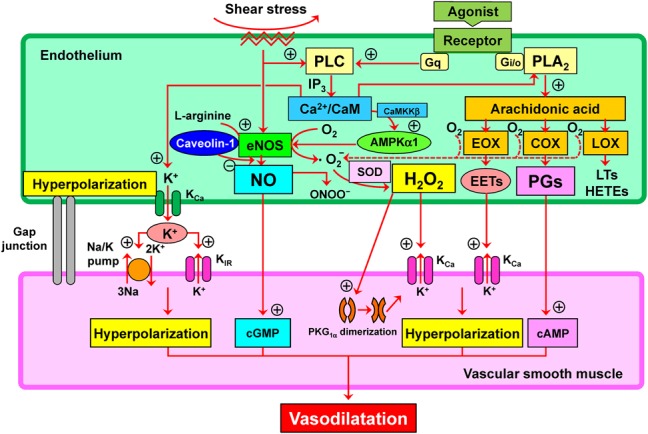
Mechanisms for synthesis and action of endothelium-derived relaxing factors in addition to vasodilator PGs and NO; several candidates could act as endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization (EDH) factor. PGs, NO, and EDH factor cause relaxations of underlying vascular smooth muscle through the mechanisms mediated by cyclic AMP (cAMP), cyclic GMP (cGMP), and hyperpolarization mediated by opening of Ca-activated K (KCa) channels. AMPKα1, α1-subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase; CaM, calmodulin; CaMKKβ, Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase β; COX, cyclooxygenase; EETs, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; eNOS, endothelial NO synthase; EOX, epoxygenase; HETEs, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; LOX, lipoxygenase; LTs, leukotrienes; ONOO−, peroxynitrite; PKG1α, 1α-subunit of protein kinase G; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PLC, phospholipase C.
