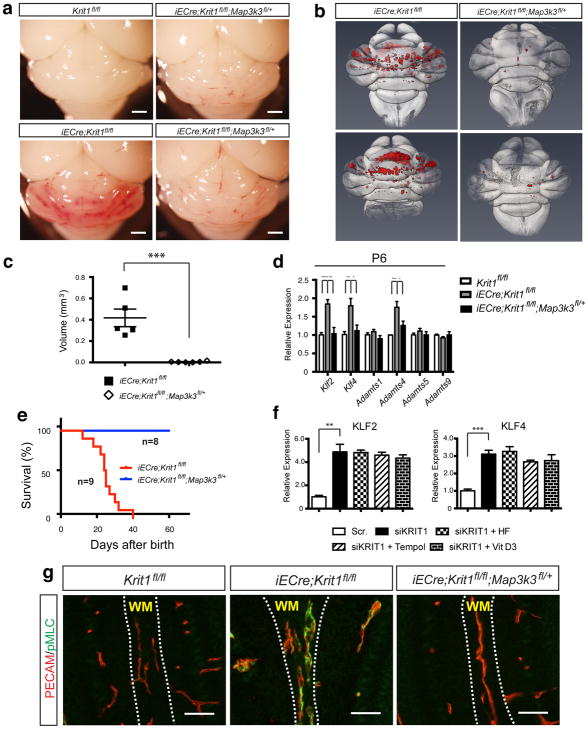
Figure 2. Genetic rescue of CCM formation and elevated Rho activity with loss of MEKK3.
a, Visual detection of CCM lesions in the hindbrains of P11 Krit1fl/fl animals (top left), Krit1ECKO animals (bottom left), and MEKK3HetRSQ animals (right). Scale bars indicate 1mm. b, Composite microCT images of Krit1ECKO and MEKK3HetRSQ hindbrains. CCM lesions are shown in red. c, Quantitation of CCM lesion volumes. N=5 for each group. d, qPCR analysis of gene expression in cerebellar endothelial cells. N=4. e, Postnatal survival of Krit1ECKO animals with and without endothelial loss of one Map3k3 allele. P=0.0009. f, qPCR analysis of gene expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells treated with scrambled (“Scr.”) or KRIT1 targeting siRNAs, alone and in the presence of the indicated Rho antagonists. HF, hydroxyfasudil. N=3. g, Normalization of Rho activity with loss of MEKK3. PECAM and pMLC staining of white matter vessels in the indicated P6 littermate brains is shown. Images are representative of 5 independent studies for each genotype. Scale bars, 50 μm. **** indicates P<0.0001; *** indicates P<0.001; ** indicates P<0.01; * indicates P<0.05. Error bars indicate SEM.