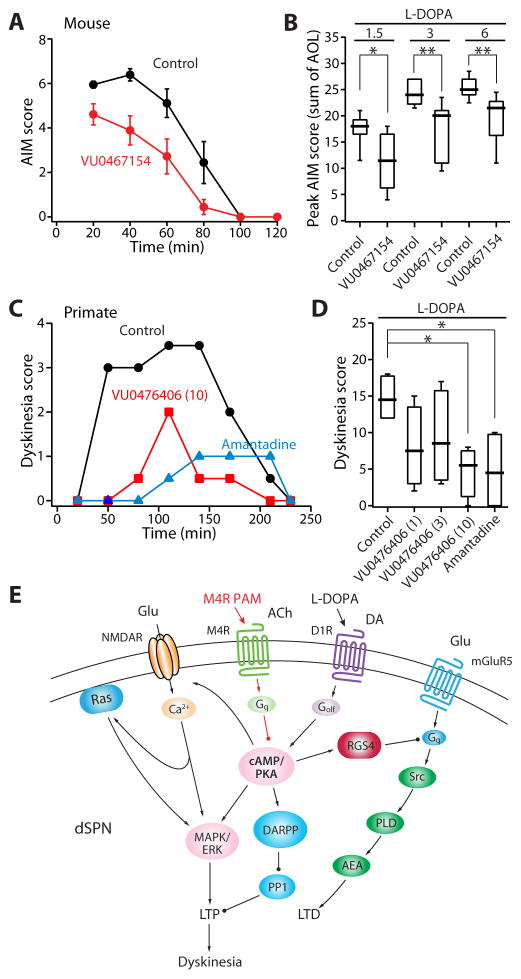
Figure 7. M4R PAMs alleviate dyskinetic behaviors.
(A) Plot of sum of mouse AIM scores (n = 9, mean ± SEM) as a function of time. Systemic treatment with VU0467154 (10 mg kg−1) produced a significant overall reduction in AIM scores (time: p < 0.001; group: p < 0.01; interaction: p < 0.01; repeated measure 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post test). (B) Box plot summation shows that VU0467154 attenuates LID behaviors over a range of L-DOPA doses. Mice were treated with ascending doses of L-DOPA combined with either the M4R PAM or its vehicle (n = 9 per group). VU0467154 was effective on each of the three L-DOPA doses (1.5, 3, or 6 mg kg−1), indicated by horizontal bars. Box plot boxes indicate upper and lower quartiles; whiskers specify upper and lower 90%. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. (C) Plot of sum of primate dyskinesia scores (median) as a function of time (Fr = 11.64, n = 4; p < 0.01, Friedman’s test). (D) Box plot summary of antidyskinetic effects of VU0476406 (1, 3, or 10 mg kg−1) or amantadine (20 mg kg−1). Systemic administration of VU0476406 (10 mg kg−1) or amantadine (20 mg kg−1) ameliorates dyskinesia scores. *p < 0.05. (E) Proposed signaling model of L-DOPA-induced deficits in dSPN synaptic plasticity and dyskinesia (see also Figures S5, S6 and S7).